Page 276 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 276
CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER 257
low void fractions, and surface temperatures in
excess of 700 C.
. What is critical heat flux in boiling heat transfer?
& Maximum heat flux achievable with nucleate boiling
is called critical heat flux.
. Give an equation for heat transfer at critical heat flux
conditions.
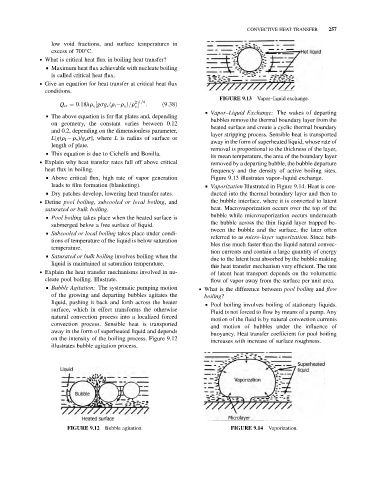
FIGURE 9.13 Vapor–liquid exchange.
2 1=4
Q cr ¼ 0:18lr ½gsg c ðr r Þ=r : ð9:38Þ
v l v v
& Vapor–Liquid Exchange: The wakes of departing
& The above equation is for flat plates and, depending
bubbles remove the thermal boundary layer from the
on geometry, the constant varies between 0.12
heated surface and create a cyclic thermal boundary
and 0.2, depending on the dimensionless parameter,
layer stripping process. Sensible heat is transported
L[g(r l r v )/g c s], where L is radius of surface or
away in the form of superheated liquid, whose rate of
length of plate.
removal is proportional to the thickness of the layer,
& This equation is due to Cichelli and Bonilla.
its mean temperature, the area of the boundary layer
. Explain why heat transfer rates fall off above critical removed by a departing bubble, the bubble departure
heat flux in boiling. frequency and the density of active boiling sites.
& Above critical flux, high rate of vapor generation Figure 9.13 illustrates vapor–liquid exchange.
leads to film formation (blanketing). & Vaporization Illustrated in Figure 9.14. Heat is con-
& Dry patches develop, lowering heat transfer rates. ducted into the thermal boundary layer and then to
. Define pool boiling, subcooled or local boiling, and the bubble interface, where it is converted to latent
saturated or bulk boiling. heat. Macrovaporization occurs over the top of the
bubble while microvaporization occurs underneath
& Pool boiling takes place when the heated surface is
the bubble across the thin liquid layer trapped be-
submerged below a free surface of liquid.
tween the bubble and the surface, the later often
& Subcooled or local boiling takes place under condi-
referred to as micro-layer vaporization. Since bub-
tions of temperature of the liquid is below saturation
bles rise much faster than the liquid natural convec-
temperature.
tion currents and contain a large quantity of energy
& Saturated or bulk boiling involves boiling when the
due to the latent heat absorbed by the bubble making
liquid is maintained at saturation temperature.
this heat transfer mechanism very efficient. The rate
. Explain the heat transfer mechanisms involved in nu- of latent heat transport depends on the volumetric
cleate pool boiling. Illustrate. flow of vapor away from the surface per unit area.
& Bubble Agitation: The systematic pumping motion . What is the difference between pool boiling and flow
of the growing and departing bubbles agitates the boiling?
liquid, pushing it back and forth across the heater & Pool boiling involves boiling of stationary liquids.
surface, which in effect transforms the otherwise
Fluid is not forced to flow by means of a pump. Any
natural convection process into a localized forced
motion of the fluid is by natural convection currents
convection process. Sensible heat is transported
and motion of bubbles under the influence of
away in the form of superheated liquid and depends
buoyancy. Heat transfer coefficient for pool boiling
on the intensity of the boiling process. Figure 9.12
increases with increase of surface roughness.
illustrates bubble agitation process.
FIGURE 9.12 Bubble agitation. FIGURE 9.14 Vaporization.