Page 146 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 146
6/126 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
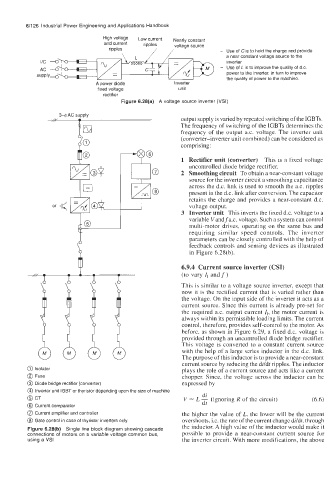
High voltage LOW current ~~~~l~ constant
and current ripples voltage source
ripples // - Use of Cis to hold the charge and provide
a near constant voltage source to the
inverter
- Use of LIS to improve the quality of d.c.
power to the inverter, in turn to improve
the quality of power to the machine.
A Dower diode Inverter
fixed voltage unit
rectifier
Figure 6.28(a) A voltage source inverter (VSI)
output supply is varied by repeated switching of the IGBTs.
The frequency of switching of the IGBTs determines the
frequency of the output a.c. voltage. The inverter unit
(converter-inverter unit combined) can be considered as
comprising:
1 Rectifier unit (converter) This is a fixed voltage
uncontrolled diode bridge rectifier.
2 Smoothing circuit To obtain a near-constant voltage
source for the inverter circuit a smoothing capacitance
across the d.c. link is used to smooth the a.c. ripples
present in the d.c. link after conversion. The capacitor
retains the charge and provides a near-constant d.c.
voltage output.
3 Inverter unit This inverts the fixed d.c. voltage to a
variable Vandfa.c. voltage. Such a system can control
multi-motor drives, operating on the same bus and
requiring similar speed controls. The inverter
parameters can be closely controlled with the help of
feedback controls and sensing devices as illustrated
in Figure 6.28(b).
6.9.4 Current source inverter (CSI)
(to vary 1, andf)
This is similar to a voltage source inverter, except that
now it is the rectified current that is varied rather than
the voltage. On the input side of the inverter it acts as a
current source. Since this current is already pre-set for
the required a.c. output current I,, the motor current is
always within its permissible loading limits. The current
control, therefore, provides self-control to the motor. As
before, as shown in Figure 6.29, a fixed d.c. voltage is
provided through an uncontrolled diode bridge rectifier.
This voltage is converted to a constant current source
with the help of a large series inductor in the d.c. link.
The purpose of this inductor is to provide a near-constant
current source by reducing the dildt ripples. The inductor
0 Isolator plays the role of a current source and acts like a current
@ Fuse chopper. Since, the voltage across the inductor can be
@ Diode bridge rectifier (converter) expressed by
@ Inverter unit IGBT or thyristor depending upon the size of machine
di .
@ CT V 2- L - (ignoring R of the circuit) (6.6)
@ Current comparator dt
@ Current amplifier and controller the higher the value of L, the lower will be the current
@ Gate control in case of thyristor inverters only. overshoots, i.e. the rate of the current change dildt, through
the inductor. A high value of the inductor would make it
Figure 6.28(b) Single line block diagram showing cascade
connections of motors on a variable voltage common bus, possible to provide a near-constant current source for
using a VSI the inverter circuit. With more modifications, the above