Page 147 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 147
Static controls and braking of motors 6/127
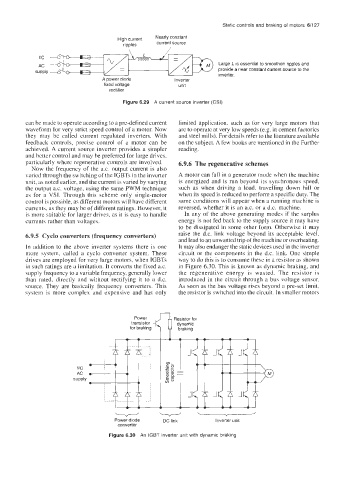
Large L IS essential to smoothen ripples and
provide a near constant current source to the
inverter.
A power diode Inverter
fixed voltage unit
rectifier
Figure 6.29 A current source inverter (CSI)
can be made to operate according to a pre-defined current limited application, such as for very large motors that
waveform for very strict speed control of a motor. Now are to operate at very low speeds (e.g. in cement factories
they may be called current regulated inverters. With and steel mills). For details refer to the literature available
feedback controls, precise control of a motor can be on the subject. A few books are mentioned in the Further
achieved. A current source inverter provides a simpler reading.
and better control and may be preferred for large drives.
particularly where regenerative controls are involved. 6.9.6 The regenerative schemes
Now the frequency of the a.c. output current is also
varied through the switching of the IGBTs in the inverter A motor can fall in a generator mode when the machine
unit, as noted earlier, and the current is varied by varying is energized and is run beyond its synchronous speed,
the output a.c. voltage, using the same PWM technique such as when driving a load. travelling down hill or
as for a VSI. Through this scheme only single-motor when its speed is reduced to perform a specific duty. The
control is possible, as different motors will have different same conditions will appear when a running machine is
currents, as they may be of different ratings. However, it reversed, whether it is an as. or a d.c. machine.
is more suitable for larger drives, as it is easy to handle In any of the above generating modes if the surplus
currents rather than voltages. energy is not fed back to the supply source it may have
to be dissipated in some other form. Otherwise it may
6.9.5 Cyclo converters (frequency converters) raise the d.c. link voltage beyond its acceptable level.
and lead to an unwanted trip of the machine or overheating.
In addition to the above inverter systems there is one It may also endanger the static devices used in the inverter
more system, called a cyclo converter system. These circuit or the components in the d.c. link. One simple
drives are employed for very large motors, when IGBTs way to do this is to consume these in a resistor as shown
in such ratings are a limitation. It converts the fixed a.c. in Figure 6.30. This is known as dynamic braking, and
supply frequency to a variable frequency, generally lower the regenerative energy is wasted. The resistor is
than rated, directly and without rectifying it to a d.c. introduced in the circuit through a bus voltage sensor.
source. They are basically frequency converters. This As soon as the bus voltage rises beyond a pre-set limit,
system is more complex and expensive and has only the resistor is switched into the circuit. in smaller motors
Power diode DC link Inverter unit
converter
Figure 6.30 An IGBT inverter unit with dynamic braking