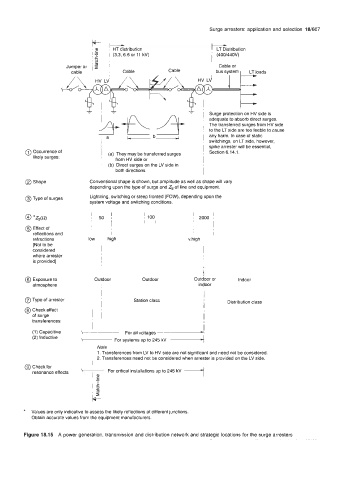
Page 642 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 642
Surge arresters: application and selection 18/607
k kstribution kstribution
I f I (3.3, 6.6 or 11 kV)
'S , I (400'440v)
Cable or
cable bus System I LT loads
I Surge protection on HV side is
, adequate to absorb direct surges.
The transferred surges from HV side
! to the LT side are too feeble to cause
any harm. In case of static
L b L
! switchings, on LT side, however,
I spike arrester will be essential,
@ Occurrence of 1 (a) They may be transferred surges I Section 6.14.1
likely surges: ' from HV side or I
(b) Direct surges on the LV side in
both directions
@ Shape Conventional shape is shown, but amplitude as well as shape will vary
depending upon the type of surge and Zs of line and equipment.
@) Type of surges Lightning, switching or steep fronted (FOW), depending upon the
system voltage and switching conditions.
I 50 I I I loo! I 2000 I I
I I
@ Effect of
reflections and I I I I
refractions low high v.high
[Not to be
considered
where arrester
is provided]
I 1
@ Exposure to Outdoor Outdoor Outdoor or Indoor
atmosphere I indoor
I
@ Type of arrester Station class Distribution class
I
@ Check effect
of surge
transferences:
I I
(1) Capacitive For all voltages ci
(2) Inductive For systems up to 245 kV -4
1 Note
I 1. Transferences from LV to HV side are not significant and need not be considered.
I 2. Transferences need not be considered when arrester is provided on the LV side.
I
@ Check for
resonance effects For critical installations up to 245 kV
IE
*
Values are only indicative to assess the likely reflections at different junctions.
Obtain accurate values from the equipment manufacturers.
Figure 18.15 A power generation, transmission and distribution network and strategic locations for the surge arresters