Page 650 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 650
Surge arresters: application and selection 18/61 5
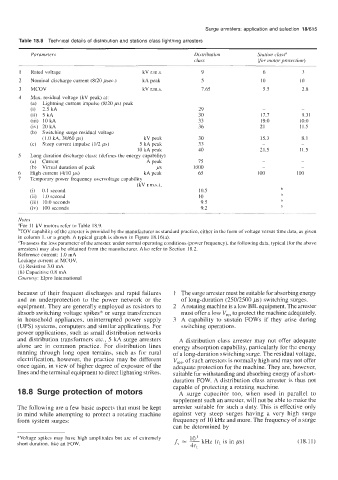
Table 18.8 Technical details of distribution and stations class lightning arresters
Parameters Distribution Station classa
class (for motor protection)
Rated voltage kV r.m.s. 9 6 3
Nominal discharge current (8120 psec.) kA peak 5 10 10
MCOV kV r.m.s. 7.65 5.5 2.8
Max. residual voltage (kV peak) at:
(a) Lightning current impulse (8120 ps) peak
(i) 2.5 kA 29 - -
(ii) 5 kA 30 17.7 9.31
(iii) IO kA 33 19.0 10.0
(iv) 20 kA 36 21 11.5
(b) Switching surge residual voltage
(1 .O kA, 30/60 ps) kV peak 30 15.3 8.1
(c) Steep current impulse (112 ps) 5 kA peak 33 - -
10 kA peak 40 21.5 11.5
Long duration discharge class: (defines the energy capability)
(a) Current A peak 75 - -
(b) Virtual duration of peak P 1000 - -
High current (4/10 ps) kA peak 65 100 100
Temporary power frequency overvoltage capability
(kV r.m.s.),
(i) 0.1 second 10.5
(ii) 1 .O second 10
(iii) 10.0 seconds 9.5
(iv) 100 seconds 9.2
Notes
"For 11 kV motors refer to Table 18.9.
bTOV capability of the arrester is provided by the manufacturer as standard practice, either in the form of voltage versus time data, as given
in column 1, or a graph. A typical graph is shown in Figure 18.16(a).
'To assess the loss parameter of the arrester, under normal operating conditions (power frequency), the following data, typical (for the above
arresters) may also be obtained from the manufacturer. Also refer to Section 18.2.
Reference current: 1 .O mA
Leakage current at MCOV,
(i) Resistive 3.0 mA
(ii) Capacitive 0.8 mA
Courtesy: Elpro International
because of their frequent discharges and rapid failures 1 The surge arrester must be suitable for absorbing energy
and an underprotection to the power network or the of long-duration (250/2500 ps) switching surges.
equipment. They are generally employed as resistors to 2 A rotating machine is a low BIL equipment. The arrester
absorb switching voltage spikes* or surge transferences must offer a low V,, to protect the machine adequately.
in household appliances, uninterrupted power supply 3 A capability to sustain FOWs if they arise during
(UPS) systems, computers and similar applications. For switching operations.
power applications, such as small distribution networks
and distribution transformers etc., 5 kA surge arresters A distribution class arrester may not offer adequate
alone are in common practice. For distribution lines energy absorption capability, particularly for the energy
running through long open terrains, such as for rural of a long-duration switching surge. The residual voltage,
electrification, however, the practice may be different V,,, of such arresters is normally high and may not offer
once again, in view of higher degree of exposure of the adequate protection for the machine. They are, however,
lines and the terminal equipment to direct lightning strikes. suitable for withstanding and absorbing energy of a short-
duration FOW. A distribution class arrester is thus not
capable of protecting a rotating machine.
18.8 Surge protection of motors A surge capacitor too, when used in parallel to
supplement such an arrester, will not be able to make the
The following are a few basic aspects that must be kept arrester suitable for such a duty. This is effective only
in mind while attempting to protect a rotating machine against very steep surges having a very high surge
from system surges: frequency of 10 kHz and more. The frequency of a surge
can be determined by
103
*Voltage spikes may have high amplitudes but are of extremely f, = - kHz (t, is in ps) (18.11)
short duration, like an FOW. 4t1