Page 487 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 487
3D TRASAR™ Technologies for Reliable Wastewater Recycling, and Reuse 457
Antiscalant dose (ppm) 5 4 3 2
6
1
0
27-Jan 1-Feb 6-Feb 11-Feb 16-Feb 21-Feb 26-Feb 2-Mar 7-Mar
Date
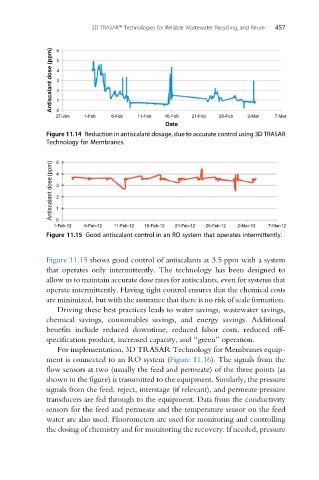
Figure 11.14 Reduction in antiscalant dosage, due to accurate control using 3D TRASAR
Technology for Membranes.
Antiscalant dose (ppm) 4 3 2
5
1
0
1-Feb-12 6-Feb-12 11-Feb-12 16-Feb-12 21-Feb-12 26-Feb-12 2-Mar-12 7-Mar-12
Figure 11.15 Good antiscalant control in an RO system that operates intermittently.
Figure 11.15 shows good control of antiscalants at 3.5 ppm with a system
that operates only intermittently. The technology has been designed to
allow us to maintain accurate dose rates for antiscalants, even for systems that
operate intermittently. Having tight control ensures that the chemical costs
are minimized, but with the assurance that there is no risk of scale formation.
Driving these best practices leads to water savings, wastewater savings,
chemical savings, consumables savings, and energy savings. Additional
benefits include reduced downtime, reduced labor costs, reduced off-
specification product, increased capacity, and “green” operation.
For implementation, 3D TRASAR Technology for Membranes equip-
ment is connected to an RO system (Figure 11.16). The signals from the
flow sensors at two (usually the feed and permeate) of the three points (as
shown in the figure) is transmitted to the equipment. Similarly, the pressure
signals from the feed, reject, interstage (if relevant), and permeate pressure
transducers are fed through to the equipment. Data from the conductivity
sensors for the feed and permeate and the temperature sensor on the feed
water are also used. Fluorometers are used for monitoring and controlling
the dosing of chemistry and for monitoring the recovery. If needed, pressure