Page 146 - Innovations in Intelligent Machines
P. 146
Evolution-based Dynamic Path Planning for Autonomous Vehicles 137
a smaller task score. The profiles of score weighting functions of both tasks
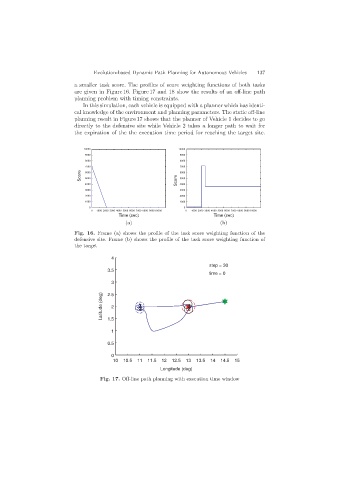
are given in Figure 16. Figure 17 and 18 show the results of an off-line path
planning problem with timing constraints.
In this simulation, each vehicle is equipped with a planner which has identi-
cal knowledge of the environment and planning parameters. The static off-line
planning result in Figure 17 shows that the planner of Vehicle 1 decides to go
directly to the defensive site while Vehicle 2 takes a longer path to wait for
the expiration of the the execution time period for reaching the target site.
10000 10000
9000 9000
8000 8000
7000 7000
Score 6000 6000
5000
5000
4000 Score 4000
3000 3000
2000 2000
1000 1000
0 0
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000
Time (sec) Time (sec)
(a) (b)
Fig. 16. Frame (a) shows the profile of the task score weighting function of the
defensive site. Frame (b) shows the profile of the task score weighting function of
the target
4
step = 30
3.5
time = 0
3
Latitude (deg) 2.5 2 1 1 2
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
10 10.5 11 11.5 12 12.5 13 13.5 14 14.5 15
Longitude (deg)
Fig. 17. Off-line path planning with execution time window