Page 495 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 495
478 Electrical measurements
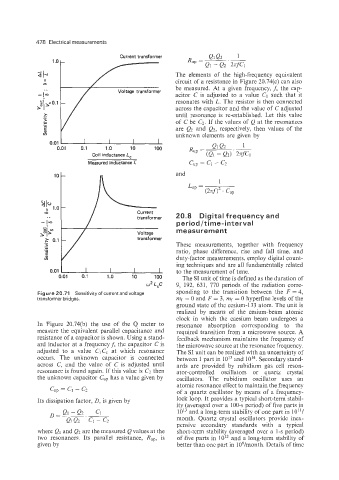
Current transformer
1.0 -
21-1 The elements of the high-frequency equivalent
circuit of a resistance in Figure 20.74(c) can also
rg
.. be measured. At a given frequency, f, the cap-
Voltage transformer
- !'.o Voltage transformer acitor C is adjusted to a value C1 such that it
t v until resonance is re-established. Let this value
- !'.o
resonates with L. The resistor is then connected
across the capacitor and the value of C adjusted
of C be C2. If the values of Q at the resonances
._
t
are (31 and
respectively, then values of the
unknown elements are given by
0.01 1
0.01 0.1 1 .o 10 100
Coil inductance L,
Measured inductance L cup = c1 - c,
and
20.8 Digital frequency and
period/time-interval
measurement
These measurements, together with frequency
ratio, phase difference, rise and fall time, and
duty-factor measurements, employ digital count-
ing techniques and are all fundamentally related
0.01 to the measurement of time.
0.01 0.1 1 .o 10 100 The SI unit of time is defined as the duration of
,2 L,C 9, 192, 631, 770 periods of the radiation corre-
Figure 20.71 Sensitivity of current and voltage sponding to the transition between the F = 4,
transformer bridges. @if = 0 and F = 3, mf = 0 hyperfine levels of the
ground state of the cesium-133 atom. The unit is
realized by means of the cesium-beam atomic
clock in which the caesium beam undergoes a
In Figure 20.74(b) the use of the Q meter to resonance absorption corresponding to the
measure the equivalent parallel capacitance and required transition from a microwave source. A
resistance of a capacitor is shown. Using a stand- feedback mechanism maintains the frequency of
ard inductor at a frequencyf, the capacitor C is the microwave source at the resonance frequency.
adjusted to a value C1CC at which resonance The SI unit can be realized with an uncertainty of
occurs. The unknown capacitor is connected between 1 part in 1013 and 1014. Secondary stand-
across C, and the value of C is adjusted until ards are provided by rubidium gas cell reson-
resonance is found again. If this value is C? then ator-controlled oscillators or quartz crystal
the unknown capacitor Cup has a value given by oscillators. The rubidium oscillator uses an
cup = c1 - c, atomic resonance effect to maintain the frequency
of a quartz oscillator by means of a frequency-
is
Its dissipation factor, D, given by lock loop. It provides a typical short-term stabil-
ity (averaged over a 100-s period) of five parts in
10" and a long-term stability of one part in lo"/
month. Quartz crystal oscillators provide inex-
pensive secondary standards with a typical
where Ql and Qz are the measured Q values at the short-term stability (averaged over a 1-s period)
two resonances. Its parallel resistance, Rup, is of five parts in 10" and a long-term stability of
given by better than one part in lO8/month. Details of time