Page 584 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 584
24 Non-destructive testing
SCOTTISH SCHOOL OF NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING
24.1 Introduction Non-destructive testing is not confined to manu-
facture. The designer and user may find applica-
The driving force for improvements and develop- tion to on-site testing of bridges, pipelines in the
ments in non-destructive testing instrumentation oil and gas industries, pressure vessels in the
is the continually increasing need to demonstrate power-generation industry, and in-service testing
the integrity and reliability of engineering mater- of nuclear plant, aircraft, and refinery installa-
ials, products, and plant. Efficient materials manu- tions. Defects at this stage may be deterioration
facture, the assurance of product quality, and in plant due to fatigue and corrosion.
re-assurance of plant at regular intervals during use The purpose of non-destructive testing during
represent the main need for non-destructive test- service is to look for deterioration in plant to
ing (NDT). This “state-of-health’’ knowledge is ensure that adequate warning is given of the need
necessary for both economic and safety reasons. to repair or replace. Periodic checks also give
Indeed, in the UK the latter reasons have been confidence that “all is well.”
strengthened by legislation such as the Health In these ways, therefore, non-destructive test-
and Safety at Work Act 1974, and in the United ing plays an important role in the manufacture
States by the Occupational Safety and Health and use of materials. Moreover, as designs
Administration (OSHA). become more adventurous and as new materials
Failures in engineering components generally are used, there is less justification for relying on
result from a combination of conditions, the main past experience. Accordingly, non-destructive
three being inadequate design, incorrect use, or testing has an increasingly important role.
the presence of defects in materials. The use of Methods of non-destructive testing are nor-
non-destructive testing seeks to eliminate the fail- mally categorized in terms of whether their suit-
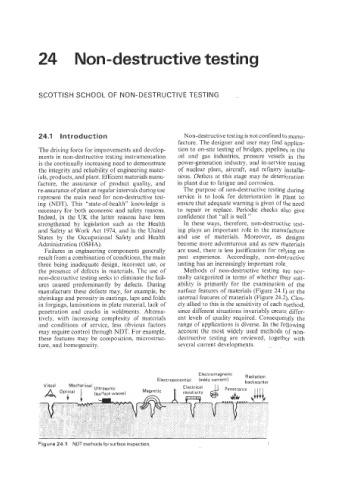
ures caused predominantly by defects. During ability is primarily for the examination of the
manufacture these defects may, for example, be surface features of materials (Figure 24.1) or the
shrinkage and porosity in castings, laps and folds internal features of materials (Figure 24.2). Clos-
in forgings, laminations in plate material, lack of ely allied to this is the sensitivity of each method,
penetration and cracks in weldments. Alterna- since different situations invariably create differ-
tively, with increasing complexity of materials ent levels of quality required. Consequently the
and conditions of service, less obvious factors range of applications is diverse. In the following
may require control through NDT. For example, account the most widely used methods of non-
these features may be composition, microstruc- destructive testing are reviewed, together with
ture, and homogeneity. several current developments.
Visual
Figure 24.1 NDT methods for surface inspection.