Page 389 - Integrated Wireless Propagation Models
P. 389
T h e l e e C o m p r e h e n s i v e M o d e l - I n t e g r a t i o n o f t h e T h r e e l e e M o d e l s 367
Micro
• 90
( ) E ) � � )
50 50 50 1 5 35 60 40
1 0 0 meters
300 meters
(a)
Micro
•
75 meters
Pi co
1 5� LJ
� � ( )
50 50 50 1 5 35 60 40
1 0 0 meters
300 meters
(b)
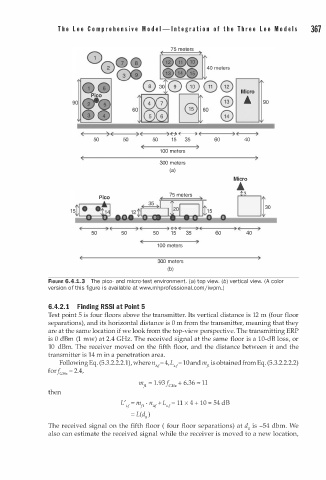
FIGURE 6.4.1.3 The pico- and micro-test environment. (a) top view. (b) vertical view. (A color
l
version of this figure is available at www.mhprofessiona . c omjiwpm. )
6.4.2. 1 Finding RSSI t Point 5
a
Test point 5 is four floors above the transmitter. Its vertical distance is 12 m (four floor
separations), and its horizontal distance is 0 m from the transmitter, meaning that they
are at the same location if we look from the top-view perspective. The transmitting ERP
is 0 dBm (1 mw) at 2.4 GHz. The received signal at the same floor is a 10-dB loss, or
10 dBm. The receiver moved on the fifth floor, and the distance between it and the
transmitter is 14 m in a penetration area.
Following Eq. (5.3.2.2.2.1), where n{; = 4 , L , = lOand m fl is obtained from Eq. (5.3.2.2.2.2)
1
1
for f cHz = 2.4,
m fl = 1 . 93 f GHz + 6.36 = 11
then
= 5
L' = m fl · n{; 1 + L ,_ = 11 x 4 + 10 4 dB
;1
1
= L (d )
0
The received signal on the fifth floor ( four floor separations) at d is -54 dbm. We
0
also can estimate the received signal while the receiver is moved to a new location,