Page 154 - System on Package_ Miniaturization of the Entire System
P. 154
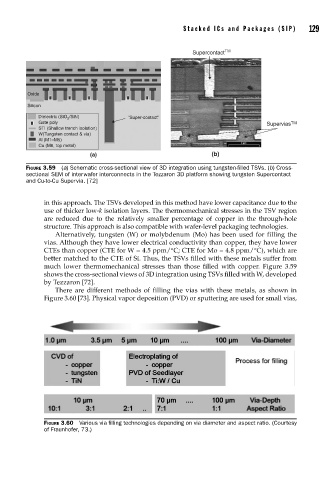
Stacked ICs and Packages (SIP) 129
Supercontact TM
Oxide
Silicon
Dielectric (SiO 2 /SiN) “Super-contact”
Gate poly Supervias TM
STI (Shallow trench isolation)
W(Tungsten contact & via)
Al (M1–M5)
Cu (M6, top metal)
(a) (b)
FIGURE 3.59 (a) Schematic cross-sectional view of 3D integration using tungsten-fi lled TSVs. (b) Cross-
sectional SEM of interwafer interconnects in the Tezzaron 3D platform showing tungsten Supercontact
and Cu-to-Cu Supervia. [72]
in this approach. The TSVs developed in this method have lower capacitance due to the
use of thicker low-k isolation layers. The thermomechanical stresses in the TSV region
are reduced due to the relatively smaller percentage of copper in the through-hole
structure. This approach is also compatible with wafer-level packaging technologies.
Alternatively, tungsten (W) or molybdenum (Mo) has been used for filling the
vias. Although they have lower electrical conductivity than copper, they have lower
CTEs than copper (CTE for W = 4.5 ppm/°C; CTE for Mo = 4.8 ppm/°C), which are
better matched to the CTE of Si. Thus, the TSVs filled with these metals suffer from
much lower thermomechanical stresses than those filled with copper. Figure 3.59
shows the cross-sectional views of 3D integration using TSVs filled with W, developed
by Tezzaron [72].
There are different methods of filling the vias with these metals, as shown in
Figure 3.60 [73]. Physical vapor deposition (PVD) or sputtering are used for small vias,
FIGURE 3.60 Various via fi lling technologies depending on via diameter and aspect ratio. (Courtesy
of Fraunhofer, 73.)