Page 270 - System on Package_ Miniaturization of the Entire System
P. 270
244 Cha pte r F o u r
calculation, a dielectric loss of tan d = 0.02 and a copper conductivity of σ = 5.8 × 10 7
c
siemens per meter (S/m) were used. The stopband predicted with Figure 4.95a is
superposed on Figure 4.95b. This figure indicates that the stopband predicted from the
dispersion diagram has good agreement with the measured and simulated data.
Two-Dimensional Unit-Cell Analysis
If the unit cells are connected with each other to form a 2D lattice, the 1D dispersion
diagram analysis becomes inaccurate, since wave propagation can be possible in any
direction on the plane in a 2D EBG, as opposed to the linear wave propagation in a 1D
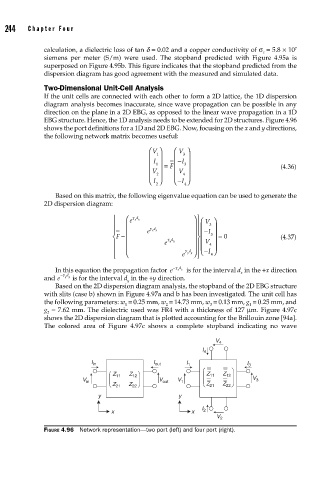
EBG structure. Hence, the 1D analysis needs to be extended for 2D structures. Figure 4.96
shows the port definitions for a 1D and 2D EBG. Now, focusing on the x and y directions,
the following network matrix becomes useful:
⎛ V ⎞ ⎛ V ⎞
⎜ 1 ⎟ ⎜ I − 3 ⎟
⎜ I 1 ⎟ = F ⎜ 3 ⎟
⎜ V ⎟ ⎜ V ⎟ (4.36)
⎜ 2 ⎟ ⎜ 4 ⎟ ⎟
I ⎝ 2 ⎠ ⎝ I − ⎠
4
Based on this matrix, the following eigenvalue equation can be used to generate the
2D dispersion diagram:
⎧ e ⎛ γ xx d ⎞ ⎫ ⎫ ⎞
⎪ ⎜ ⎟ ⎪ ⎛ V 3 ⎟
⎜
⎪ ⎜ e γ xx d ⎟ ⎪ −I ⎟
⎜
⎨ F − ⎜ γ ⎟ ⎬ 3 = 0 (4.37)
⎪ ⎜ e yy d ⎟ ⎪ ⎜ V 4 ⎟ ⎟
⎜
⎪ ⎜ γ yy d ⎟ ⎪ − ⎠
⎝ I
⎩ ⎝ e ⎠ ⎭ 4
−γ xx d
In this equation the propagation factor e is for the interval d in the +x direction
x
−γ yy d
and e is for the interval d in the +y direction.
y
Based on the 2D dispersion diagram analysis, the stopband of the 2D EBG structure
with slits (case b) shown in Figure 4.97a and b has been investigated. The unit cell has
the following parameters: w = 0.25 mm, w = 14.73 mm, w = 0.13 mm, g = 0.25 mm, and
2
1
1
3
g = 7.62 mm. The dielectric used was FR4 with a thickness of 127 μm. Figure 4.97c
2
shows the 2D dispersion diagram that is plotted accounting for the Brillouin zone [94a].
The colored area of Figure 4.97c shows a complete stopband indicating no wave
V 4
I 4
I in I out I 1 I 3
Z 11 Z 12 Z 11 Z 12
V in V out V 1 V 3
Z 21 Z 22 Z 21 Z 22
y y
I
x x 2
V 2
FIGURE 4.96 Network representation—two port (left) and four port (right).