Page 200 - Marks Calculation for Machine Design
P. 200
P1: Shibu
January 4, 2005
Brown˙C04
Brown.cls
182
U.S. Customary 14:25 STRENGTH OF MACHINES SI/Metric
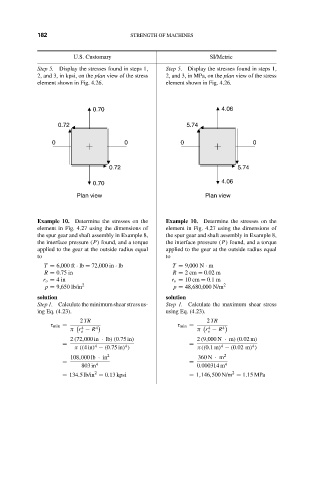
Step 5. Display the stresses found in steps 1, Step 5. Display the stresses found in steps 1,
2, and 3, in kpsi, on the plan view of the stress 2, and 3, in MPa, on the plan view of the stress
element shown in Fig. 4.26. element shown in Fig. 4.26.
0.70 4.06
0.72 5.74
0 0 0 0
0.72 5.74
0.70 4.06
Plan view Plan view
Example 10. Determine the stresses on the Example 10. Determine the stresses on the
element in Fig. 4.27 using the dimensions of element in Fig. 4.27 using the dimensions of
the spur gear and shaft assembly in Example 8, the spur gear and shaft assembly in Example 8,
the interface pressure (P) found, and a torque the interface pressure (P) found, and a torque
applied to the gear at the outside radius equal applied to the gear at the outside radius equal
to to
T = 6,000 ft · lb = 72,000 in · lb T = 9,000 N · m
R = 0.75 in R = 2cm = 0.02 m
r o = 4in r o = 10 cm = 0.1 m
p = 9,650 lb/in 2 p = 48,680,000 N/m 2
solution solution
Step 1. Calculate the minimum shear stress us- Step 1. Calculate the maximum shear stress
ing Eq. (4.23). using Eq. (4.23).
2 TR 2 TR
τ min = τ min =
4
4
π r − R 4 π r − R 4
o o
2 (72,000 in · lb)(0.75 in) 2 (9,000 N · m)(0.02 m)
= 4 4 = 4 4
π((4in) − (0.75 in) ) π((0.1m) − (0.02 m) )
108,000 lb · in 2 360 N · m 2
= =
803 in 4 0.000314 m 4
2
2
= 134.5 lb/in = 0.13 kpsi = 1,146,500 N/m = 1.15 MPa