Page 127 - Mechanical Engineers Reference Book
P. 127
I Inverter T+5V +5 v
3/10 Microprocessors, instrumentation and control
..i, Load supply
e
1
I
Supply Computer Darlington
r
voltage input driver
signal
a
-
Relay Load
supply
voltage
(+I 2 V)
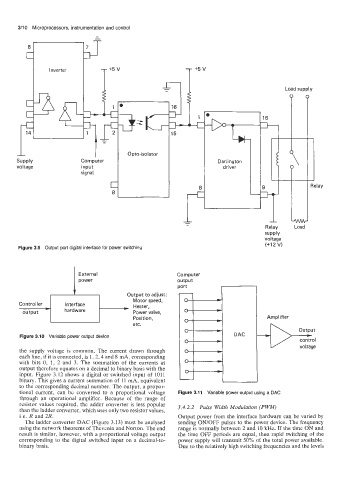
Figure 3.9 Output port digital interface for power switching
External
power
port
Output to adjust: 7
Motor speed, 0 *
Interface Heater,
0
output hardware Power valve, 0 -
).
Position, 0 - Amplifier
etc.
Figure 3.10 Variable power output device DAC
0 -
0 *
the supply voltage is common. The current drawn through 0 m voltage
each line, if it is connected, is 1,2,4 and 8 mA, corresponding
with bits 0, 1, 2 and 3. The summation of the currents at 0 -
output therefore equates on a decimal to binary basis with the
input. Figure 3.12 shows a digital or switched input of 1011
binary. This gives a current summation of 11 mA, equivalent d 1
to the corresponding decimal number. The output, a propor-
tional current, can be converted to a proportional voltage Figure 3.11 Variable power output using a DAC
through an operational amplifier. Because of the range of
resistor values required, the adder converter is less popular 3.4.2.2 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
than the ladder converter, which uses only two resistor values,
i.e. R and 2R. Output power from the interface hardware can be varied by
The ladder converter DAC (Figure 3.13) must be analysed sending ON/OFF pulses to the power device. The frequency
using the network theorems of Thevenin and Norton. The end range is normally between 2 and 10 kHz. If the time ON and
result is similar, however, with a proportional voltage output the time OFF periods are equal, then rapid switching of the
corresponding to the digital switched input on a decimal-to- power supply will transmit 50% of the total power available.
binary basis. Due to the relatively high switching frequencies and the levels