Page 254 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 254
5 Flip-Flops 243
{LUTin}
a b
C out SRAM
1 00
D
LUT
0 01
f
D 1 10 {LUTout}
LUT
1 11
C in
Figure 3 A two-input LUT implementing the function ƒ a b.
the output ƒ. The contents of the memory cells are calculated from the evaluation of ƒ a
b for all the combinations of logic values of a and b.
5 FLIP-FLOPS
Flip-flop devices are used in the digital field for a variety of purposes such as storing data
temporarily, multiplication or division, counting, or receiving and transferring information.
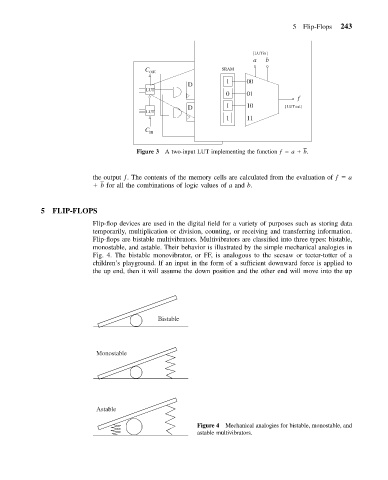
Flip-flops are bistable multivibrators. Multivibrators are classified into three types: bistable,
monostable, and astable. Their behavior is illustrated by the simple mechanical analogies in
Fig. 4. The bistable monovibrator, or FF, is analogous to the seesaw or teeter-totter of a
children’s playground. If an input in the form of a sufficient downward force is applied to
the up end, then it will assume the down position and the other end will move into the up
Bistable
Monostable
Astable
Figure 4 Mechanical analogies for bistable, monostable, and
astable multivibrators.