Page 305 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 305
.. .
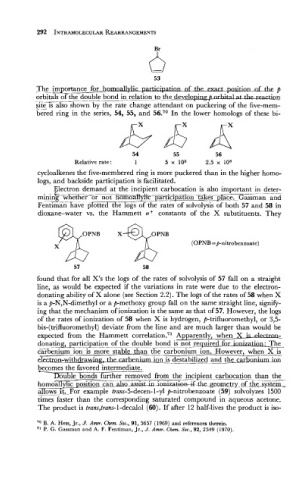
Th_e importance for hodylic of-*&
p
_
.
brbitals of -___ the double bond in relatmvelop- on
$2 1s also shown by the rate change attendant on puckering of the five-mem-
bered ring in the series, 54, 55, and 56.70 In the lower homologs of these bi-
54 55 56
Relative rate: 1 5 x loa 2.5 x lo6
cycloalkenes the five-membered ring is more puckered than in the higher homo-
logs, and backside is facilitated.
Electron demand at the incipient carbocation is also important in deter-
L - --
mining whether or not homoaiiyiic paxTFpafion -fiilie~FJltTe~sman and
~ektGZiri.ha;e proft~Flogs of the rates of solvolysis of both 57 and 58 in
dioxane-water vs. the Hammett o+ constants of the X substituents. They
found that for all X's the logs of the rates of solvolysis of 57 fall on a straight
line, as would be expected if the variations in rate were due to the electron-
donating ability of X alone (see Section 2.2). The logs of the rates of 58 when X
is a p-N,N-dimethyl or a p-methoxy group fall on the same straight line, signify-
ing that the mechanism of ionization is the same as that of 57. However, the logs
of the rates of ionization of 58 when X is hydrogen, p-trifluoromethyl, or 3,5-
bis-(trifluoromethyl) deviate from the line and are much larger than would be
expected from the Hammett ~orrelation.~~ Apparently, when X is ~Jer.tmn-
donating, participation of the ~. double bond is not required for ianization: The
.
.
-.
cXfb&nium ion is more stable than the carbonium ion. However, .~he," is,
and
electron-withdr~~larhenium~njs~d_estabilized the carb.aiumian
becomes the favored intermediate. -.
Double bonds further removed from the - incipient carbocation than the
--
---
.
..
homo~llylic position ca~alsso-assistin ~~~~thegenmme_tryyof tJ~~ystem.,
allows it. For example tram-5-decen-l-yl p-nitrobenzoate (59) solvolyzes 1500
times faster than the corresponding saturated compound in aqueous acetone.
The product is traqtram- l-decal01 (60). If after 12 half-lives the product is iso-
B. A. Hess, Jr., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 91, 5657 (1969) and references therein.
P. G. Gassman and A. F. Fentiman, Jr., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 92, 2549 (1970).