Page 187 -
P. 187
5.2 Theoretical Analysis 177
(a) 150 (b) 150
Length (nm) 100 Length (nm) 100
50
0 50
0
50 100 150 200 250 50 100 150 200 250
(c) 150
Length (nm) 100
50
Boundary 0
50 100 150 200 250
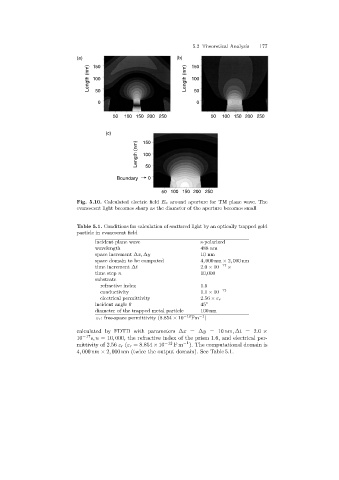
Fig. 5.10. Calculated electric field E x around aperture for TM plane wave. The
evanescent light becomes sharp as the diameter of the aperture becomes small
Table 5.1. Conditions for calculation of scattered light by an optically trapped gold
particle in evanescent field
incident plane wave s-polarized
wavelength 488 nm
space increment ∆x, ∆y 10 nm
space domain to be computed 4, 000 nm × 2, 000 nm
time increment ∆t 2.0 × 10 −17 s
time step n 10,000
substrate
refractive index 1.6
conductivity 1.1 × 10 −12
electrical permittivity 2.56 × ε r
incident angle θ 45 ◦
diameter of the trapped metal particle 100 nm
ε r: free-space permittivity (8.854 × 10 −12 Fm −1 )
calculated by FDTD with parameters ∆x =∆y =10 nm, ∆t =2.0 ×
10 −17 s,n =10, 000, the refractive index of the prism 1.6, and electrical per-
mittivity of 2.56 ε r (ε r =8.854 × 10 −12 Fm −1 ). The computational domain is
4, 000 nm × 2, 000 nm (twice the output domain). See Table 5.1.