Page 195 -
P. 195
5.3 Experimental Analysis 185
[5.20]. Accordingto the theoretical analysis, surface refractive index distrib-
ution mappingwith a high contrast is predicted to be possible [5.7]. A metal
particle probe is considered to have the advantages of high experimental re-
producibility, not requiringgap control, and not only the ability to obtain the
surface image, but also to obtain the spectroscopic data of the sample. The
scattering efficiency of a silver particle is higher than that of a gold particle,
but the latter is more chemically stable. Therefore a gold particle is frequently
used as an SNOM probe.
Sugiura et al. [5.8] observed a dip on a cover glass and a gold colloidal
particle adhering to the cover glass. However, these images were thought to
have been an artifact problem due to the vertical displacement of the gold
probe [5.12]. On the other hand, the followingare observed for a refractive
index grating on a flat surface, which was made on a planar light waveguide
circuit (PLC) [5.24], by scanningan optically trapped 100-nm-diameter gold
+
particle. The scattered Ar laser light from the gold particle has a high inten-
sity due to the high refractive index of the grating with periods of 1.06 and
0.53 µm, both by s- and p-polarized illuminations.
Moreover, the surface profile of an optical disk trackinggroove is also
observed with and without the gold particle and the results compared to
discuss the artificial effect due to the vertical displacement of the particle
caused by the surface topology.
Experimental Setup
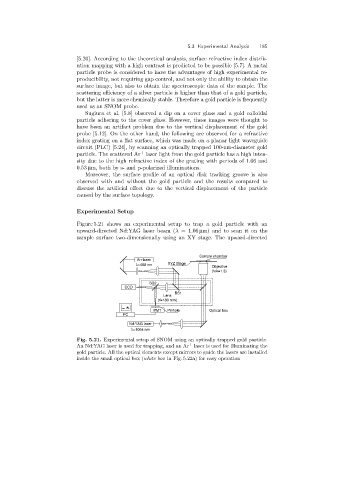
Figure 5.21 shows an experimental setup to trap a gold particle with an
upward-directed Nd:YAG laser beam (λ =1.06 µm) andtoscanitonthe
sample surface two-dimensionally usingan XY stage. The upward-directed
Sample chamber
Ar+laser
XYZ Stage
l=488 nm
Objective
(NA=1.3)
BS2
CCD
BS1
Lens
(f=180 mm)
PMT Pinhole Optical box
PC
Nd:YAG laser
l=1064 nm
Fig. 5.21. Experimental setup of SNOM using an optically trapped gold particle.
+
An Nd:YAG laser is used for trapping, and an Ar laser is used for illuminating the
gold particle. All the optical elements except mirrors to guide the lasers are installed
inside the small optical box (white box in Fig. 5.22a)for easy operation