Page 145 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 145
ETCH-STOP TECHNIQUES 125
(EDP), and hydrazine (see Table 5.2). Because of the heavy boron-doping, the lattice
constant of silicon decreases slightly, leading to highly strained membranes that often
show slip planes. They are, however, taut and fairly rugged even in a few microns of
thickness and are approximately 1 cm in diameter. The technique is not suited to stress-
sensitive microstructures that could lead to the movement of the structures without an
external load. In this case, other etch-stop methods should be employed.
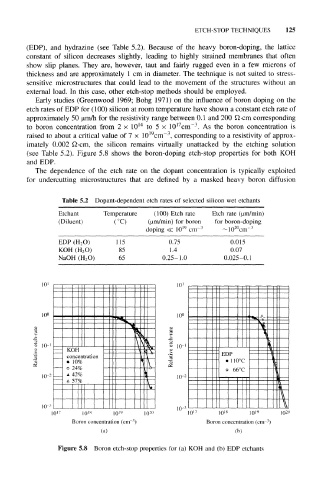
Early studies (Greenwood 1969; Bohg 1971) on the influence of boron doping on the
etch rates of EDP for (100) silicon at room temperature have shown a constant etch rate of
approximately 50 u,rn/h for the resistivity range between 0.1 and 200 Q-cm corresponding
–3
17
to boron concentration from 2 × 10 14 to 5 x 10 cm . As the boron concentration is
19
–3
raised to about a critical value of 7 × 10 cm , corresponding to a resistivity of approx-
imately 0.002 £2-cm, the silicon remains virtually unattacked by the etching solution
(see Table 5.2). Figure 5.8 shows the boron-doping etch-stop properties for both KOH
and EDP.
The dependence of the etch rate on the dopant concentration is typically exploited
for undercutting microstructures that are defined by a masked heavy boron diffusion
Table 5.2 Dopant-dependent etch rates of selected silicon wet etchants
Etchant Temperature (100) Etch rate Etch rate (urn/min)
(Diluent) (°C) (um/min) for boron for boron-doping
20
doping «; 10 19 cm –3 ~10 cm –3
EDP (H 2O) 115 0.75 0.015
KOH (H 2O) 85 1.4 0.07
NaOH (H 2O) 65 0.25-1.0 0.025-0.1
1
10
10 –1
KOH
concentration
• 10%
o 24%
A 42%
A 57%
10
10 17 10 18 10 19 10 18 10 19
–3
Boron concentration (c Boron concentration (cm )
(a) (b)
Figure 5.8 Boron etch-stop properties for (a) KOH and (b) EDP etchants