Page 225 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 225
POLYMERIC MEMS ARCHITECTURE 205
Z indicator
Actuator
Lapping plate
\ \ Electrolyte
K-stage X-stage Electrolyte
(b)
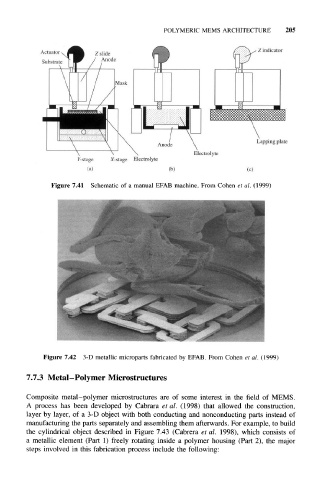
Figure 7.41 Schematic of a manual EFAB machine. From Cohen et al. (1999)
Figure 7.42 3-D metallic microparts fabricated by EFAB. From Cohen et al. (1999)
7.7.3 Metal–Polymer Microstructures
Composite metal-polymer microstructures are of some interest in the field of MEMS.
A process has been developed by Cabrara et al. (1998) that allowed the construction,
layer by layer, of a 3-D object with both conducting and nonconducting parts instead of
manufacturing the parts separately and assembling them afterwards. For example, to build
the cylindrical object described in Figure 7.43 (Cabrera et al. 1998), which consists of
a metallic element (Part 1) freely rotating inside a polymer housing (Part 2), the major
steps involved in this fabrication process include the following: