Page 227 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 227
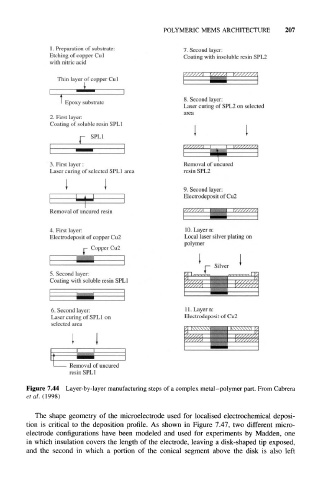
POLYMERIC MEMS ARCHITECTURE 207
1. Preparation of substrate: 7. Second layer:
Etching of copper Cul Coating with insoluble resin SPL2
with nitric acid
Thin layer of copper Cu 1
8. Second layer:
I Epoxy substrate
Laser curing of SPL2 on selected
area
2. First layer:
Coating of soluble resin SPL1
SPL1
3. First layer: Removal of uncured
Laser curing of selected SPL1 area resin SPL2
9. Second layer:
Electrodeposit of Cu2
Removal of uncured resin
4. First layer: 10. Layer n:
Electrodeposit of copper Cu2 Local laser silver plating on
polymer
Copper Cu2
5. Second layer:
Coating with soluble resin SPL1
6. Second layer: 11. Layer n:
Laser curing of SPL1 on Electrodeposit of Cu2
selected area
Removal of uncured
resin SPL1
Figure 7.44 Layer-by-layer manufacturing steps of a complex metal-polymer part. From Cabrera
et al. (1998)
The shape geometry of the microelectrode used for localised electrochemical deposi-
tion is critical to the deposition profile. As shown in Figure 7.47, two different micro-
electrode configurations have been modeled and used for experiments by Madden, one
in which insulation covers the length of the electrode, leaving a disk-shaped tip exposed,
and the second in which a portion of the conical segment above the disk is also left