Page 321 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 321
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 5 CHARACTERIZATION METHODS FOR NANOSTRUCTURE OF MATERIALS
Figure 5.3.28
Temperature dependence of contact angle of liquid Sn on (1 1 0) plane of diamond.
Table 5.3.4
Work of adhesion between liquid metal and magnesia single
crystal.
–2
Metal Work of adhesion (ergcm )
(1 0 0) plane (1 1 1) plane (1 1 0) plane
Sn 121 84 8
Pb 97 63 14
Bi 88 52 32
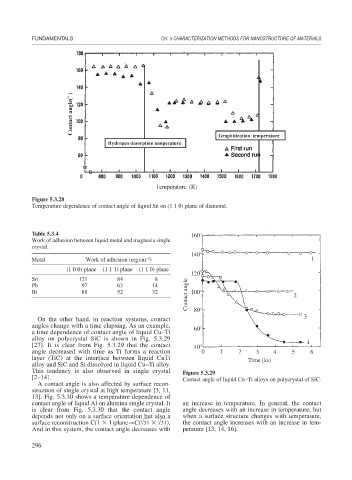
On the other hand, in reaction systems, contact
angles change with a time elapsing. As an example,
a time dependence of contact angle of liquid Cu–Ti
alloy on polycrystal SiC is shown in Fig. 5.3.29
[27]. It is clear from Fig. 5.3.29 that the contact
angle decreased with time as Ti forms a reaction
layer (TiC) at the interface between liquid CuTi
alloy and SiC and Si dissolved in liquid Cu–Ti alloy.
This tendency is also observed in single crystal Figure 5.3.29
[2–14]. Contact angle of liquid Cu–Ti alloys on polycrystal of SiC.
A contact angle is also affected by surface recon-
struction of single crystal at high temperature [3, 11,
13]. Fig. 5.3.30 shows a temperature dependence of
contact angle of liquid Al on alumina single crystal. It an increase in temperature. In general, the contact
is clear from Fig. 5.3.30 that the contact angle angle decreases with an increase in temperature, but
depends not only on a surface orientation but also a when a surface structure changes with temperature,
surface reconstruction C(1 1)plane C( 3 1 31). the contact angle increases with an increase in tem-
And in this system, the contact angle decreases with perature [13, 14, 16].
296