Page 112 - Power Electronic Control in Electrical Systems
P. 112
//SYS21/F:/PEC/REVISES_10-11-01/075065126-CH003.3D ± 100 ± [82±105/24] 17.11.2001 9:53AM
100 Transmission system compensation
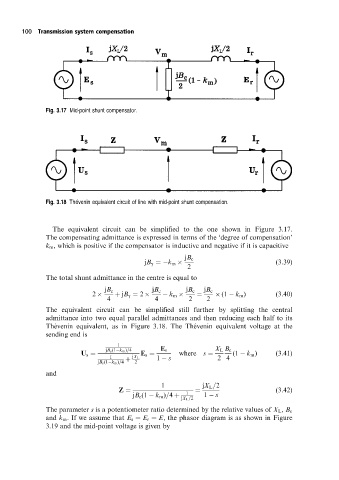
Fig. 3.17 Mid-point shunt compensator.
Â
Fig. 3.18 Thevenin equivalent circuit of line with mid-point shunt compensation.
The equivalent circuit can be simplified to the one shown in Figure 3.17.
The compensating admittance is expressed in terms of the `degree of compensation'
k m , which is positive if the compensator is inductive and negative if it is capacitive
jB c
jB g k m (3:39)
2
The total shunt admittance in the centre is equal to
jB c jB c jB c jB c
2 jB g 2 k m (1 k m ) (3:40)
4 4 2 2
The equivalent circuit can be simplified still further by splitting the central
admittance into two equal parallel admittances and then reducing each half to its
The  venin equivalent, as in Figure 3.18. The The  venin equivalent voltage at the
sending end is
1
jB c (1 k m )=4 E s X L B c
U s E s where s (1 k m ) (3:41)
1 jX L 1 s 2 4
jB c (1 k m )=4 2
and
1 jX L =2
Z 1 (3:42)
jB c (1 k m )=4 1 s
jX L =2
The parameter s is a potentiometer ratio determined by the relative values of X L , B c
and k m . If we assume that E s E r E, the phasor diagram is as shown in Figure
3.19 and the mid-point voltage is given by