Page 294 - Power Electronic Control in Electrical Systems
P. 294
//SYS21/F:/PEC/REVISES_10-11-01/075065126-CH007.3D ± 282 ± [263±289/27] 17.11.2001 10:25AM
282 Harmonic studies of power compensating plant
1994), give results for a TCSC module with the following parameters, C 212 mF
and L 15 mH, a line current of 2000 A and a firing angle of 133 .
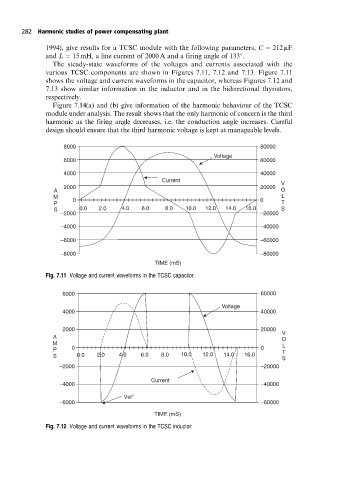
The steady-state waveforms of the voltages and currents associated with the
various TCSC components are shown in Figures 7.11, 7.12 and 7.13. Figure 7.11
shows the voltage and current waveforms in the capacitor, whereas Figures 7.12 and
7.13 show similar information in the inductor and in the bidirectional thyristors,
respectively.
Figure 7.14(a) and (b) give information of the harmonic behaviour of the TCSC
module under analysis. The result shows that the only harmonic of concern is the third
harmonic as the firing angle decreases, i.e. the conduction angle increases. Careful
design should ensure that the third harmonic voltage is kept at manageable levels.
8000 80000
Voltage
6000 60000
4000 40000
Current V
2000 20000
A O
M 0 0 L
P T
.
.
.
S 0.0 2 0 4 0 6. 0 8. 0 10.0 12 0 14.0 16.0 S
–2000 –20000
–4000 –40000
–6000 –60000
–8000 –80000
TIME (mS)
Fig. 7.11 Voltage and current waveforms in the TCSC capacitor.
6000 60000
Voltage
4000 40000
2000 20000
V
A O
M L
P 0 0 T
S 0.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0 12.0 14.0 16.0
S
–2000 –20000
Current
–4000 –40000
Vst"
–6000 –60000
TIME (mS)
Fig. 7.12 Voltage and current waveforms in the TCSC inductor.