Page 32 - Principles and Applications of NanoMEMS Physics
P. 32
18 Chapter 1
1.2.2.2 Bulk Micromachining
As the name implies, bulk micromachining sculpts the substrate itself to
form the 3-D mechanical structure. The simplest example of this technique is
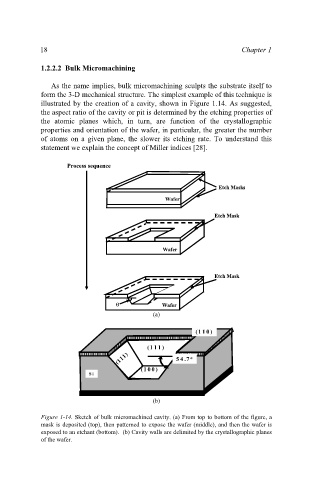
illustrated by the creation of a cavity, shown in Figure 1.14. As suggested,
the aspect ratio of the cavity or pit is determined by the etching properties of
the atomic planes which, in turn, are function of the crystallographic
properties and orientation of the wafer, in particular, the greater the number
of atoms on a given plane, the slower its etching rate. To understand this
statement we explain the concept of Miller indices [28].
Process sequence
Process sequence
Etch Masks
Etch Masks
Wafer
Wafer
Etch Mask
Etch Mask
Wafer
Wafer
Etch Mask
Etch Mask
θ θ Wafer
Wafer
(a)
(110)
(110)
(111)
(111)
(111)
(111) 54.7 o o
54.7
(1 00)
(1 00)
Si
Si
(b)
Figure 1-14. Sketch of bulk micromachined cavity. (a) From top to bottom of the figure, a
mask is deposited (top), then patterned to expose the wafer (middle), and then the wafer is
exposed to an etchant (bottom). (b) Cavity walls are delimited by the crystallographic planes
of the wafer.