Page 39 - Principles and Applications of NanoMEMS Physics
P. 39
1. NANOELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS 25
D
I
R
P
I
L L IQ U ID P R E CUR S O R T O P D M S S
U
Q
E
P
O
M
D
S
CUR
R T
O
MASTER
(a)
M
PD M S STAMP
M
PHOTO RES IST
(b) (c)
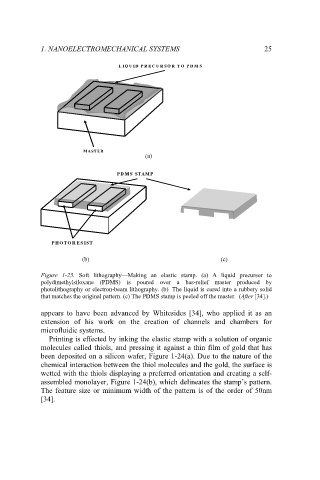
Figure 1-23. Soft lithography—Making an elastic stamp. (a) A liquid precursor to
polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is poured over a bas-relief master produced by
photolithography or electron-beam lithography. (b) The liquid is cured into a rubbery solid
that matches the original pattern. (c) The PDMS stamp is peeled off the master. (After [34].)
(
(
appears to have been advanced by Whitesides [34], who applied it as an
extension of his work on the creation of channels and chambers for
microfluidic systems.
Printing is effected by inking the elastic stamp with a solution of organic
molecules called thiols, and pressing it against a thin film of gold that has
been deposited on a silicon wafer, Figure 1-24(a). Due to the nature of the
chemical interaction between the thiol molecules and the gold, the surface is
wetted with the thiols displaying a preferred orientation and creating a self-
assembled monolayer, Figure 1-24(b), which delineates the stamp’s pattern.
The feature size or minimum width of the pattern is of the order of 50nm
[34].