Page 143 - Rashid, Power Electronics Handbook
P. 143
9 Static Induction Devices 131
much narrower potential barrier can be obtained when other
types of emitter are used. There are two well-known emitters:
(1) p-n junction (Fig. 9.10a); and (2) Schottky junction (Fig.
9.10b). For silicon devices p-n junctions have a forward
voltage drop of 0.7–0.8 V while Schottky emitters have 0.2–
0.3 V only. As the Schottky diode is a majority carrier device,
carrier storage effect is negligible.
Another interesting emitter structure is shown in Fig. 9.10c.
This emitter has all the advantages of the Schottky diode even
though it is fabricated out of p-n junctions.
The concept of static induction devices can be used inde-
pendently of the type of emitter shown in Fig. 9.10. With
Schottky type and punch-through type emitters the poten-
tial barrier is much narrower and this results in faster response
time and larger current gain in the bipolar mode of
operation.
9.6 Static Induction Diode (SID)
The bipolar mode of operation of SIT also can be used to
obtain diodes with low forward voltage drop and negligible
carrier storage effect [2, 5, 13, 23, 24]. A static induction diode
can be obtained by shorting a gate to the emitter of the static
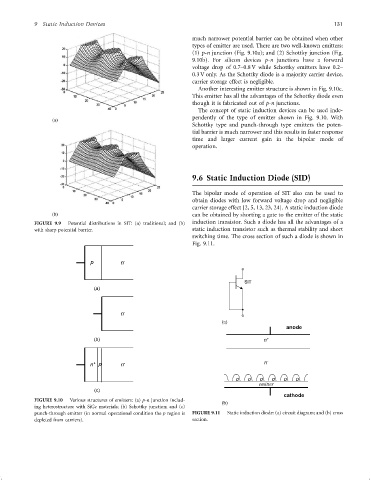
FIGURE 9.9 Potential distributions in SIT: (a) traditional; and (b) induction transistor. Such a diode has all the advantages of a
with sharp potential barrier. static induction transistor such as thermal stability and short
switching time. The cross section of such a diode is shown in
Fig. 9.11.
p n -
SIT
(a)
n -
(a)
anode
(b) n +
n + p n - n -
p p p p p p
emitter
(c)
cathode
FIGURE 9.10 Various structures of emitters: (a) p-n junction includ-
(b)
ing heterostructure with SiGe materials; (b) Schottky junction; and (c)
punch-through emitter (in normal operational condition the p region is FIGURE 9.11 Static induction diode: (a) circuit diagram; and (b) cross
depleted from carriers). section.