Page 228 - Rashid, Power Electronics Handbook
P. 228
13 DC-DC Converters 217
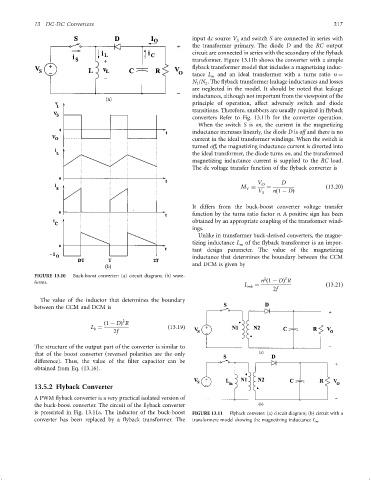
input dc source V and switch S are connected in series with
S
the transformer primary. The diode D and the RC output
circuit are connected in series with the secondary of the ¯yback
transformer. Figure 13.11b shows the converter with a simple
¯yback transformer model that includes a magnetizing induc-
tance L m and an ideal transformer with a turns ratio n ¼
N /N . The ¯yback transformer leakage inductances and losses
2
1
are neglected in the model. It should be noted that leakage
inductances, although not important from the viewpoint of the
principle of operation, affect adversely switch and diode
transitions. Therefore, snubbers are usually required in ¯yback
converters Refer to Fig. 13.11b for the converter operation.
When the switch S is on, the current in the magnetizing
inductance increases linearly, the diode D is off and there is no
current in the ideal transformer windings. When the switch is
turned off, the magnetizing inductance current is diverted into
the ideal transformer, the diode turns on, and the transformed
magnetizing inductance current is supplied to the RC load.
The dc voltage transfer function of the ¯yback converter is
V O D
M ¼ ð13:20Þ
V
V S nð1 ÿ DÞ
It differs from the buck-boost converter voltage transfer
function by the turns ratio factor n. A positive sign has been
obtained by an appropriate coupling of the transformer wind-
ings.
Unlike in transformer buck-derived converters, the magne-
tizing inductance L of the ¯yback transformer is an impor-
m
tant design parameter. The value of the magnetizing
inductance that determines the boundary between the CCM
and DCM is given by
FIGURE 13.10 Buck-boost converter: (a) circuit diagram; (b) wave- 2
2
n ð1 ÿ DÞ R
forms.
L mb ¼ ð13:21Þ
2f
The value of the inductor that determines the boundary
between the CCM and DCM is
2
ð1 ÿ DÞ R
L ¼ ð13:19Þ
b
2f
The structure of the output part of the converter is similar to
that of the boost converter (reversed polarities are the only
difference). Thus, the value of the ®lter capacitor can be
obtained from Eq. (13.16).
13.5.2 Flyback Converter
A PWM ¯yback converter is a very practical isolated version of
the buck-boost converter. The circuit of the ¯yback converter
is presented in Fig. 13.11a. The inductor of the buck-boost FIGURE 13.11 Flyback conveter: (a) circuit diagram; (b) circuit with a
converter has been replaced by a ¯yback transformer. The transformere model showing the magnetizing inductance L m .