Page 119 - Renewable Energy Devices and System with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS
P. 119
106 Renewable Energy Devices and Systems with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS ®
®
The RCC MPPT method exhibits a fast response, but its operation is based on the existence
of switching ripples, which might be undesirable during the operation of power converters. Also,
the performance of this MPPT technique is affected by the accuracy of the measurements of the
correlation function, c t().
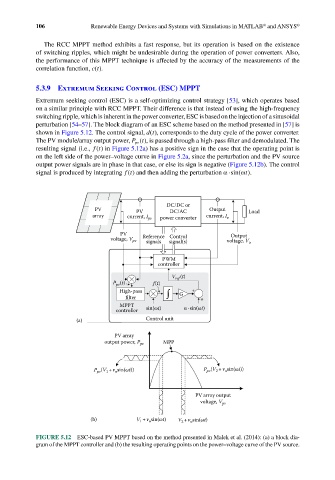
5.3.9 Extremum Seeking Control (ESC) MPPT
Extremum seeking control (ESC) is a self-optimizing control strategy [53], which operates based
on a similar principle with RCC MPPT. Their difference is that instead of using the high- frequency
switching ripple, which is inherent in the power converter, ESC is based on the injection of a sinusoidal
perturbation [54–57]. The block diagram of an ESC scheme based on the method presented in [57] is
shown in Figure 5.12. The control signal, d t(), corresponds to the duty cycle of the power converter.
The PV module/array output power, Pt(), is passed through a high-pass filter and demodulated. The
pv
resulting signal (i.e., f t() in Figure 5.12a) has a positive sign in the case that the operating point is
on the left side of the power–voltage curve in Figure 5.2a, since the perturbation and the PV source
output power signals are in phase in that case, or else its sign is negative (Figure 5.12b). The control
signal is produced by integrating f t() and then adding the perturbation α⋅sin( ω ).
t
DC/DC or
PV PV DC/AC Output Load
array current, I pv power converter current, I o
PV Output
voltage, V pv Reference Control voltage, V o
signals
signal(s)
PWM
controller
V (t)
ref
P (t) f(t)
pv
High-pass G +
filter +
MPPT
controller sin(ωt) α·sin(ωt)
(a) Control unit
PV array
output power, P pv MPP
P (V +v sin(ωt)) P (V +v sin(ωt))
o
2
pv
1
o
pv
PV array output
voltage, V pv
(b) V +v sin(ωt) V +v sin(ωt)
1
o
o
2
FIGURE 5.12 ESC-based PV MPPT based on the method presented in Malek et al. (2014): (a) a block dia-
gram of the MPPT controller and (b) the resulting operating points on the power–voltage curve of the PV source.