Page 80 - Science at the nanoscale
P. 80
7:6
RPS: PSP0007 - Science-at-Nanoscale
June 12, 2009
From Atoms and Molecules to Nanoscale Materials
70
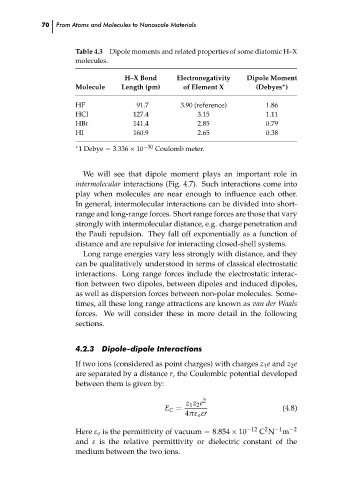
Table 4.3 Dipole moments and related properties of some diatomic H–X
molecules.
Electronegativity
H–X Bond
Length (pm)
of Element X
∗
Molecule
(Debyes )
3.90 (reference)
91.7
1.86
HF
127.4
3.15
HCl
1.11
0.79
2.85
HBr
141.4
0.38
160.9
HI
2.65
−30
1 Debye = 3.336 × 10
Coulomb meter.
∗
We will see that dipole moment plays an important role in
intermolecular interactions (Fig. 4.7). Such interactions come into
play when molecules are near enough to influence each other.
In general, intermolecular interactions can be divided into short-
range and long-range forces. Short range forces are those that vary
strongly with intermolecular distance, e.g. charge penetration and
the Pauli repulsion. They fall off exponentially as a function of
distance and are repulsive for interacting closed-shell systems.
Long range energies vary less strongly with distance, and they
can be qualitatively understood in terms of classical electrostatic
interactions. Long range forces include the electrostatic interac-
tion between two dipoles, between dipoles and induced dipoles,
as well as dispersion forces between non-polar molecules. Some-
times, all these long range attractions are known as van der Waals
forces. We will consider these in more detail in the following
sections.
4.2.3 Dipole-dipole Interactions Dipole Moment ch04
If two ions (considered as point charges) with charges z 1 e and z 2 e
are separated by a distance r, the Coulombic potential developed
between them is given by:
z 1 z 2 e 2
E C = (4.8)
4πε o εr
2
Here ε o is the permittivity of vacuum = 8.854 × 10 −12 C N −1 m −2
and ε is the relative permittivity or dielectric constant of the
medium between the two ions.