Page 124 - Separation process principles 2
P. 124
3.3 One-Dimensional, Steady-State and Unsteady-State, Molecular Diffusion through Stationary Media 89
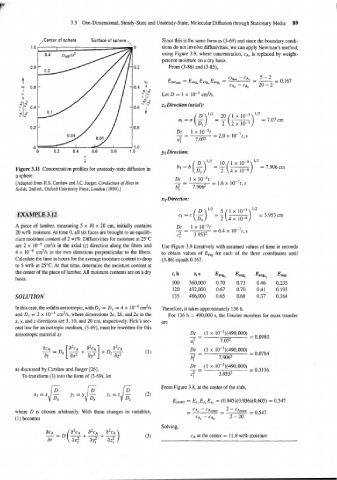
,Center of sphere Surface of sphere, Since this is the same form as (3-69) and since the boundary condi-
tions do not involve diffusivities, we can apply Newman's method,
using Figure 3.9, where concentration, c~, is replaced by weight-
percent moisture on a dry basis.
From (3-86) and (3-85),
Let D = 1 x lo-' cm2/s.
zl Direction (axial):
y 1 Direction:
-
a 10 1 x 'I2
Figure 3.11 Concentration profiles for unsteady-state diffusion in b = b ( = - ( 4 x lo-6 = 7.906 cm
2
a sphere.
~t 1 103
s
[Adapted from H.S. Carslaw and J.C. Jaeger, Conduction of Heat in -- - = 1.6 x l~-~t,
Solids, 2nd ed., Oxford University Press, London (1959).] b: 7.9062
EXAMPLE 3.12
A piece of lumber, measuring 5 x 10 x 20 cm, initially contains
20 wt% moisture. At time 0, all six faces are brought to an equilib-
rium moisture content of 2 wt%. Diffusivities for moisture at 25°C
are 2 x lo-' cm2/s in the axial (z) direction along the fibers and Use Figure 3.9 iteratively with assumed values of time in seconds
4 x lop6 cm2/s in the two directions perpendicular to the fibers. to obtain values of Eavg for each of the three coordinates until
Calculate the time in hours for the average moisture content to drop (3-86) equals 0.167.
to 5 wt% at 25OC. At that time, determine the moisture content at
the center of the piece of lumber. All moisture contents are on a dry
basis.
SOLUTION
In this case, the solid is anisotropic, with Dx = D, = 4 x low6 cm2/s Therefore, it takes approximately 136 h.
and D, = 2 x lo-' cm2/s, where dimensions 2c, 2b, and 2a in the For 136 h = 490,000 s, the Fourier numbers for mass transfer
x, y, and z directions are 5, 10, and 20 cm, respectively. Fick's sec- are
ond law for an isotropic medium, (3-69), must be rewritten for this
Dt
anisotropic material as - - (1 x 10-5)(490,000) = 0.0980
-
a? 7.072
as discussed by Carslaw and Jaeger 1261.
To transform (1) into the form of (3-69), let
From Figure 3.8, at the center of the slab,
Ecen., = E,, E,, Ex, = (0.945)(0.956)(0.605) = 0.547
where D is chosen arbitrarily. With these changes in variables,
(1) becomes
Solving,
(3) CA at the center = 11.8 wt% moisture