Page 239 - Separation process principles 2
P. 239
204 Chapter 6 Absorption and Stripping of Dilute Mixtures
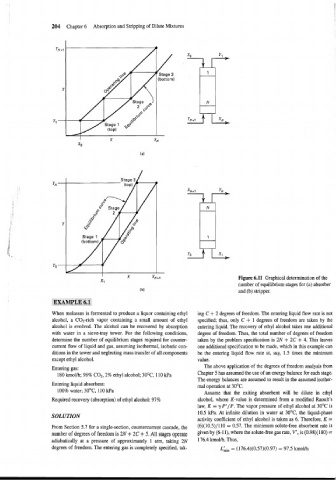
Figure 6.11 Graphical determination of the
number of equilibrium stages for (a) absorber
and (b) stripper.
When molasses is fermented to produce a liquor containing ethyl ing C + 2 degrees of freedom. The entering liquid flow rate is not
alcohol, a C02-rich vapor containing a small amount of ethyl specified; thus, only C + 1 degrees of freedom are taken by the
alcohol is evolved. The alcohol can be recovered by absorption entering liquid. The recovery of ethyl alcohol takes one additional
with water in a sieve-tray tower. For the following conditions, degree of freedom. Thus, the total number of degrees of freedom
determine the number of equilibrium stages required for counter- taken by the problem specification is 2N + 2C + 4. This leaves
current flow of liquid and gas, assuming isothermal, isobaric con- one additional specification to be made, which in this example can
ditions in the tower and neglecting mass transfer of all components be the entering liquid flow rate at, say, 1.5 times the minimum
except ethyl alcohol. value.
The above application of the degrees of freedom analysis from
Entering gas:
180 kmollh; 98% COz, 2% ethyl alcohol; 30°C, 110 kPa Chapter 5 has assumed the use of an energy balance for each stage.
The energy balances are assumed to result in the assumed isother-
Entering liquid absorbent:
mal operation at 30°C.
100% water; 30°C, 110 kPa Assume that the exiting absorbent will be dilute in ethyl
Required recovery (absorption) of ethyl alcohol: 97% alcohol, whose K-value is determined from a modified Raoult's
law, K = y PS/P. The vapor pressure of ethyl alcohol at 30°C is
10.5 kPa. At infinite dilution in water at 30°C, the liquid-phase
SOLUTZON
activity coefficient of ethyl alcohol is taken as 6. Therefore, K =
From Section 5.7 for a single-section, countercurrent cascade, the (6)(10.5)/110 = 0.57. The minimum solute-free absorbent rate is
number of degrees of freedom is 2N t 2C t 5. All stages operate given by (6-ll), where the solute-free gas rate, V', is (0.98)(180) =
adiabatically at a pressure of approximately 1 atm, taking 2N 176.4 kmolth. Thus,
degrees of freedom. The entering gas is completely specified, tak-