Page 57 - Using ANSYS for Finite Element Analysis A Tutorial for Engineers
P. 57
44 • Using ansys for finite element analysis
125 37 5 −875
.
.
.
−75 −250 43 75
.
.
T
B
D
∴[] []=3 6923 125 37 5 875
.
75 250 43.775
− 250 − 75 0
87 5
0 0 − .
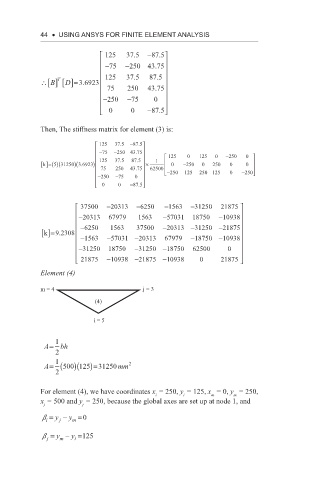
Then, The stiffness matrix for element (3) is:
125 37 5 . −875 .
.
−75 −250 43 75 125 0 125 5 0 − 250 0
)
.
5
k []=()(31250 )(3 6923 125 37 5 . 875 . × 1 0 − 250 0 250 0 0
.
75 5 250 43 75 62500 − − 250
− 250 − 75 0 250 125 250 125 0
0 0 − 87 5 .
37500 −20313 −6250 −1563 −31250 21875
−
−20313 67979 1563 −557031 18750 10938
− 6250 1563 37500 − 20313 − 31250 − 21875
k []=9 2308
.
− 1563 − 570331 − 20313 67979 − 18750 − 10938
− 31250 18750 − 31250 − 18750 62500 0
218775 − 10938 − 21875 − 10938 0 21875
Element (4)
m = 4 j = 3
(4)
i = 5
A= 1 bh
2
1 2
A= (500 )(125 )=31250 mm
2
For element (4), we have coordinates x = 250, y = 125, x = 0, y = 250,
i
m
m
i
x = 500 and y = 250, because the global axes are set up at node 1, and
j
j
b = y − y =0
i
j
m
b = y − y =125
j
m
i