Page 58 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 58
2.3 MOS Logic 43
EXAMPLE 2.2
Use SPICE to determine the effect of finite rise and fall times of the input signal
for the same CMOS inverter as in Example 2.1. Particularly, study the effect on
propagation time and power consumption.
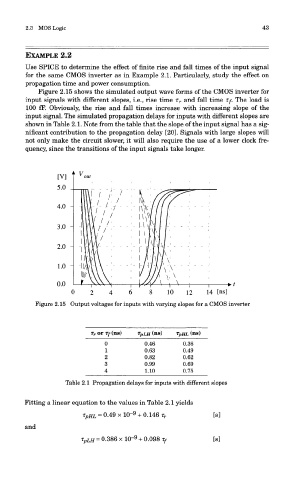
Figure 2.15 shows the simulated output wave forms of the CMOS inverter for
input signals with different slopes, i.e., rise time r r and fall time if. The load is
100 fF. Obviously, the rise and fall times increase with increasing slope of the
input signal. The simulated propagation delays for inputs with different slopes are
shown in Table 2.1. Note from the table that the slope of the input signal has a sig-
nificant contribution to the propagation delay [20]. Signals with large slopes will
not only make the circuit slower, it will also require the use of a lower clock fre-
quency, since the transitions of the input signals take longer.
Figure 2.15 Output voltages for inputs with varying slopes for a CMOS inverter
T r or Tf (ns) r pLH (ns) T pHL (ns)
0 0.46 0.36
1 0.63 0.49
2 0.82 0.62
3 0.99 0.69
4 1.10 0.75
Table 2.1 Propagation delays for inputs with different slopes
Fitting a linear equation to the values in Table 2.1 yields
and