Page 66 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 66
2.4 VLSI Process Technologies 51
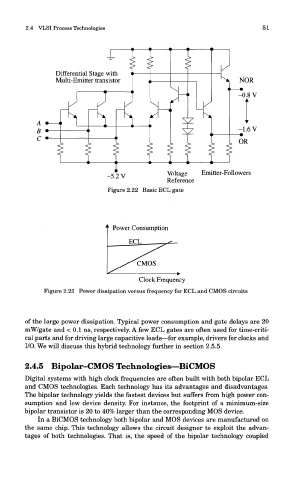
Figure 2.22 Basic ECL gate
Figure 2.23 Power dissipation versus frequency for ECL and CMOS circuits
of the large power dissipation. Typical power consumption and gate delays are 20
mW/gate and < 0.1 ns, respectively. A few ECL gates are often used for time-criti-
cal parts and for driving large capacitive loads—for example, drivers for clocks and
I/O. We will discuss this hybrid technology further in section 2.5.5.
2.4.5 Bipolar-CMOS Technologies—BiCMOS
Digital systems with high clock frequencies are often built with both bipolar ECL
and CMOS technologies. Each technology has its advantages and disadvantages.
The bipolar technology yields the fastest devices but suffers from high power con-
sumption and low device density. For instance, the footprint of a minimum-size
bipolar transistor is 20 to 40% larger than the corresponding MOS device.
In a BiCMOS technology both bipolar and MOS devices are manufactured on
the same chip. This technology allows the circuit designer to exploit the advan-
tages of both technologies. That is, the speed of the bipolar technology coupled