Page 576 - Dynamics of Mechanical Systems
P. 576
0593_C16_fm Page 557 Tuesday, May 7, 2002 7:06 AM
Mechanical Components: Cams 557
v
a
Cam Follower Velocity Cam Follower Acceleration
m
2
1
1 2
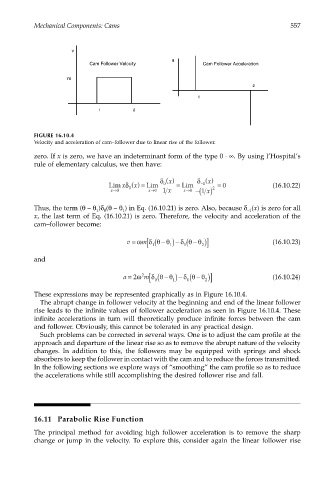
FIGURE 16.10.4
Velocity and acceleration of cam–follower due to linear rise of the follower.
zero. If x is zero, we have an indeterminant form of the type 0 ⋅ ∞. By using l’Hospital’s
rule of elementary calculus, we then have:
δ x () δ x ()
δ
Limx () = Lim 0 = Lim −1 = 0 (16.10.22)
x
0
x→0 x→0 1 x x→0 −(1 x) 2
Thus, the term (θ – θ )δ (θ – θ ) in Eq. (16.10.21) is zero. Also, because δ (x) is zero for all
1
–1
1
0
x, the last term of Eq. (16.10.21) is zero. Therefore, the velocity and acceleration of the
cam–follower become:
v = ω δ θ θ δ − )] (16.10.23)
− ) − (θ θ
m ( [ 1
1 1 2
and
a = 2ω 2 δ θ θ δ − )] (16.10.24)
− ) − (θ θ
m ( [ 0
1 0 2
These expressions may be represented graphically as in Figure 16.10.4.
The abrupt change in follower velocity at the beginning and end of the linear follower
rise leads to the infinite values of follower acceleration as seen in Figure 16.10.4. These
infinite accelerations in turn will theoretically produce infinite forces between the cam
and follower. Obviously, this cannot be tolerated in any practical design.
Such problems can be corrected in several ways. One is to adjust the cam profile at the
approach and departure of the linear rise so as to remove the abrupt nature of the velocity
changes. In addition to this, the followers may be equipped with springs and shock
absorbers to keep the follower in contact with the cam and to reduce the forces transmitted.
In the following sections we explore ways of “smoothing” the cam profile so as to reduce
the accelerations while still accomplishing the desired follower rise and fall.
16.11 Parabolic Rise Function
The principal method for avoiding high follower acceleration is to remove the sharp
change or jump in the velocity. To explore this, consider again the linear follower rise