Page 577 - Dynamics of Mechanical Systems
P. 577
0593_C16_fm Page 558 Tuesday, May 7, 2002 7:06 AM
558 Dynamics of Mechanical Systems
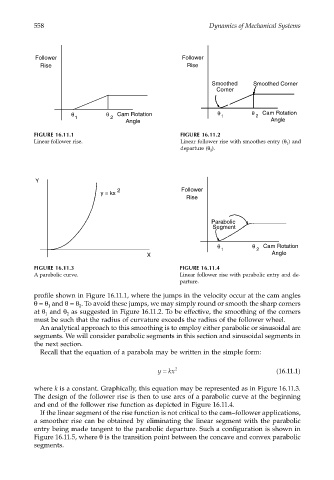
Follower Follower
Rise Rise
Smoothed Smoothed Corner
Corner
θ θ Cam Rotation θ θ Cam Rotation
1 2 1 2
Angle Angle
FIGURE 16.11.1 FIGURE 16.11.2
Linear follower rise. Linear follower rise with smoothes entry (θ 1 ) and
departure (θ 2 ).
Y
2 Follower
y = kx
Rise
Parabolic
Segment
θ θ Cam Rotation
1 2
X Angle
FIGURE 16.11.3 FIGURE 16.11.4
A parabolic curve. Linear follower rise with parabolic entry and de-
parture.
profile shown in Figure 16.11.1, where the jumps in the velocity occur at the cam angles
θ = θ and θ = θ . To avoid these jumps, we may simply round or smooth the sharp corners
1
2
at θ and θ as suggested in Figure 16.11.2. To be effective, the smoothing of the corners
1
2
must be such that the radius of curvature exceeds the radius of the follower wheel.
An analytical approach to this smoothing is to employ either parabolic or sinusoidal arc
segments. We will consider parabolic segments in this section and sinusoidal segments in
the next section.
Recall that the equation of a parabola may be written in the simple form:
y = kx 2 (16.11.1)
where k is a constant. Graphically, this equation may be represented as in Figure 16.11.3.
The design of the follower rise is then to use arcs of a parabolic curve at the beginning
and end of the follower rise function as depicted in Figure 16.11.4.
If the linear segment of the rise function is not critical to the cam–follower applications,
a smoother rise can be obtained by eliminating the linear segment with the parabolic
entry being made tangent to the parabolic departure. Such a configuration is shown in
Figure 16.11.5, where θ is the transition point between the concave and convex parabolic
segments.