Page 275 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 275
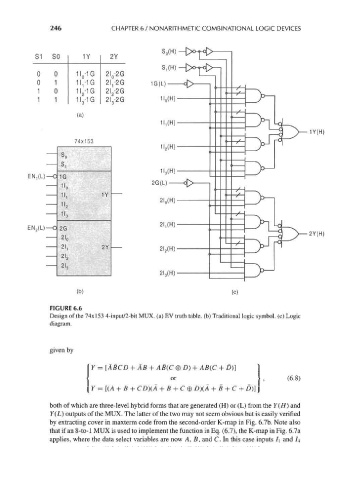
246 CHAPTER 6 / NONARITHMETIC COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DEVICES
S 0(H)
bl £>U i y ZY
0 0 11 -1G 2L-2G
0 0
0 1 11,-IG 21^20
1 0 1I 2 -1G 2I 2-2G
1 1 1I 3 -1G 2I 3-2G
(a)
___ 1Y(H)
Ti l I I M -^
74x153
EN^L)- 1G
I'o
11, 1Y
1I 2
11,
EN 2(L) 2G
2Y(H)
rrcn—\ i HdK^
2Y
2I 2
21 3
(b) (c)
FIGURE 6.6
Design of the 74x153 4-input/2-bit MUX. (a) EV truth table, (b) Traditional logic symbol, (c) Logic
diagram.
given by
Y = [ABCD + AB + AB(C 0 D) + AB(C + D)]
or (6.8)
Y = [(A + B + CD)(A + B + C® D)(A + B + C + D)]
both of which are three-level hybrid forms that are generated (H) or (L) from the Y(H) and
Y(L) outputs of the MUX. The latter of the two may not seem obvious but is easily verified
by extracting cover in maxterm code from the second-order K-map in Fig. 6.7b. Note also
that if an 8-to-l MUX is used to implement the function in Eq. (6.7), the K-map in Fig. 6.7a
applies, where the data select variables are now A, B, and C. In this case inputs I\ and /4