Page 392 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 392
8.8 ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC UNITS 363
B 2(H) A 2(H) B^H) A^H) B 0(H) A 0(H)
Carry
ton-1
stage
2 C 2 G 1 P t C, G 0 P 0 C 0
CGP Network of Figure 8.13
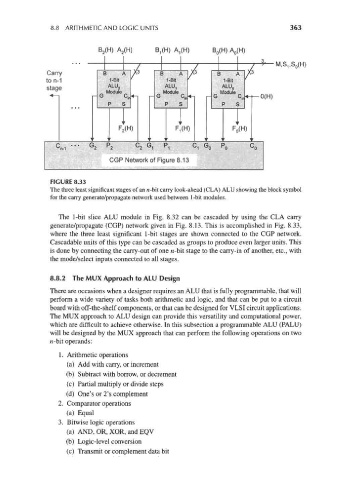
FIGURE 8.33
The three least significant stages of an n-bit carry look-ahead (CLA) ALU showing the block symbol
for the carry generate/propagate network used between 1-bit modules.
The 1-bit slice ALU module in Fig. 8.32 can be cascaded by using the CLA carry
generate/propagate (CGP) network given in Fig. 8.13. This is accomplished in Fig. 8.33,
where the three least significant 1-bit stages are shown connected to the CGP network.
Cascadable units of this type can be cascaded as groups to produce even larger units. This
is done by connecting the carry-out of one n-bit stage to the carry-in of another, etc., with
the mode/select inputs connected to all stages.
8.8.2 The MUX Approach to ALU Design
There are occasions when a designer requires an ALU that is fully programmable, that will
perform a wide variety of tasks both arithmetic and logic, and that can be put to a circuit
board with off-the-shelf components, or that can be designed for VLSI circuit applications.
The MUX approach to ALU design can provide this versatility and computational power,
which are difficult to achieve otherwise. In this subsection a programmable ALU (PALU)
will be designed by the MUX approach that can perform the following operations on two
n-bit operands:
1. Arithmetic operations
(a) Add with carry, or increment
(b) Subtract with borrow, or decrement
(c) Partial multiply or divide steps
(d) One's or 2's complement
2. Comparator operations
(a) Equal
3. Bitwise logic operations
(a) AND, OR, XOR, and EQV
(b) Logic-level conversion
(c) Transmit or complement data bit