Page 478 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 478
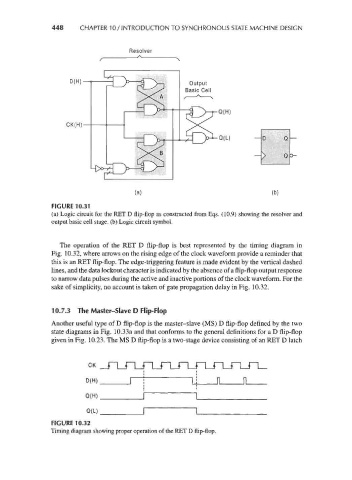
448 CHAPTER 10 / INTRODUCTION TO SYNCHRONOUS STATE MACHINE DESIGN
Resolver
D(H)
-Q(H)
~~ k"-^
CK(H)-
_ rv-^N
•Q(L)
(a) (b)
FIGURE 10.31
(a) Logic circuit for the RET D flip-flop as constructed from Eqs. (10.9) showing the resolver and
output basic cell stage, (b) Logic circuit symbol.
The operation of the RET D flip-flop is best represented by the timing diagram in
Fig. 10.32, where arrows on the rising edge of the clock waveform provide a reminder that
this is an RET flip-flop. The edge-triggering feature is made evident by the vertical dashed
lines, and the data lockout character is indicated by the absence of a flip-flop output response
to narrow data pulses during the active and inactive portions of the clock waveform. For the
sake of simplicity, no account is taken of gate propagation delay in Fig. 10.32.
10.7.3 The Master-Slave D Flip-Flop
Another useful type of D flip-flop is the master-slave (MS) D flip-flop defined by the two
state diagrams in Fig. 10.33a and that conforms to the general definitions for a D flip-flop
given in Fig. 10.23. The MS D flip-flop is a two-stage device consisting of an RET D latch
CK
D(H)
Q(H)
Q(L)
FIGURE 10.32
Timing diagram showing proper operation of the RET D flip-flop.