Page 487 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 487
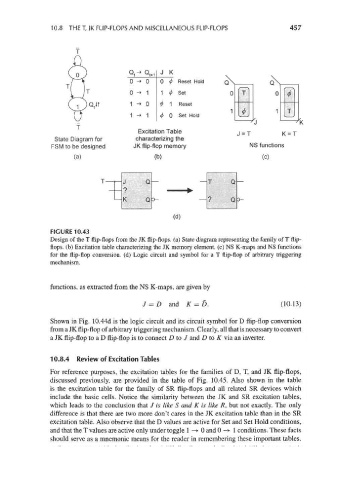
10.8 THE T, JK FLIP-FLOPS AND MISCELLANEOUS FLIP-FLOPS 457
J K
0*1
o -» o 0 <j> Reset Hold
0 -» 1 1 ^ Set
1 -» 0 ^ 1 Reset
1 -» 1 ^ 0 Set Hold
Excitation Table J= T K= T
State Diagram for characterizing the
FSM to be designed JK flip-flop memory NS functions
(a) (b) (c)
(d)
FIGURE 10.43
Design of the T flip-flops from the JK flip-flops, (a) State diagram representing the family of T flip-
flops, (b) Excitation table characterizing the JK memory element, (c) NS K-maps and NS functions
for the flip-flop conversion, (d) Logic circuit and symbol for a T flip-flop of arbitrary triggering
mechanism.
functions, as extracted from the NS K-maps, are given by
J = D and K = D. (10.13)
Shown in Fig. 10.44d is the logic circuit and its circuit symbol for D flip-flop conversion
from a JK flip-flop of arbitrary triggering mechanism. Clearly, all that is necessary to convert
a JK flip-flop to a D flip-flop is to connect D to J and D to K via an inverter.
10.8.4 Review of Excitation Tables
For reference purposes, the excitation tables for the families of D, T, and JK flip-flops,
discussed previously, are provided in the table of Fig. 10.45. Also shown in the table
is the excitation table for the family of SR flip-flops and all related SR devices which
include the basic cells. Notice the similarity between the JK and SR excitation tables,
which leads to the conclusion that J is like S and K is like R, but not exactly. The only
difference is that there are two more don't cares in the JK excitation table than in the SR
excitation table. Also observe that the D values are active for Set and Set Hold conditions,
and that the T values are active only under toggle 1 -> 0 and 0 -> 1 conditions. These facts
should serve as a mnemonic means for the reader in remembering these important tables.