Page 616 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 616
586 CHAPTER 12 / MODULE AND BIT-SLICE DEVICES
Pj(H)
CO(H)-/ CI(H)
~1 < It "Hi * M. P--' D/U(H)
r ^ 1
I
V,J
LD(L)-c|> r{>o-^
EN(H)_[>o T^>—
• • •
/
' rl '
/ / \
\ y"
\ 1 J— — C LD PA PB PC PD
X
^
\ \. EN CL
± CL(L) D/g 4-bit Parallel
CK-0 loadable up/down
\s D V counter
<CL J CO Cl
Q Q QA Q B Q c Q 0
v
Qj(H)
(a) »)
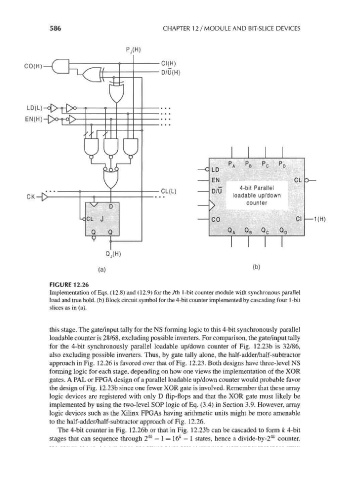
FIGURE 12.26
Implementation of Eqs. (12.8) and (12.9) for the /th 1-bit counter module with synchronous parallel
load and true hold, (b) Block circuit symbol for the 4-bit counter implemented by cascading four 1-bit
slices as in (a).
this stage. The gate/input tally for the NS forming logic to this 4-bit synchronously parallel
loadable counter is 28/68, excluding possible inverters. For comparison, the gate/input tally
for the 4-bit synchronously parallel loadable up/down counter of Fig. 12.23b is 32/86,
also excluding possible inverters. Thus, by gate tally alone, the half-adder/half-subtractor
approach in Fig. 12.26 is favored over that of Fig. 12.23. Both designs have three-level NS
forming logic for each stage, depending on how one views the implementation of the XOR
gates. A PAL or FPGA design of a parallel loadable up/down counter would probable favor
the design of Fig. 12.23b since one fewer XOR gate is involved. Remember that these array
logic devices are registered with only D flip-flops and that the XOR gate must likely be
implemented by using the two-level SOP logic of Eq. (3.4) in Section 3.9. However, array
logic devices such as the Xilinx FPGAs having arithmetic units might be more amenable
to the half-adder/half-subtractor approach of Fig. 12.26.
The 4-bit counter in Fig. 12.26b or that in Fig. 12.23b can be cascaded to form k 4-bit
4i
4k
stages that can sequence through 2 — 1 = 16* — 1 states, hence a divide-by-2 counter.