Page 618 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 618
588 CHAPTER 12 / MODULE AND BIT-SLICE DEVICES
Pj(H)
H
CQ(H) \-( [_, ^_ ii 1 C| (_ )
D/U(H)
EN(H)
LD(L)-o(
EN NS,
Qj True Hold
(CNT), Count
(a) (b)
CK-o(>o
CL(L)
Qj(H)
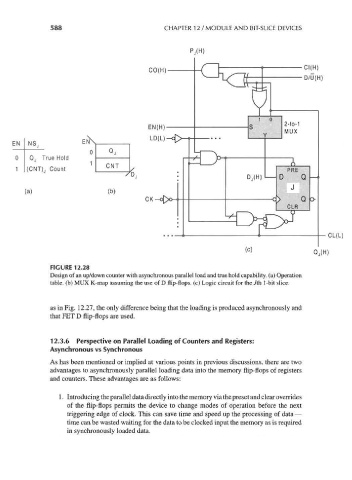
FIGURE 12.28
Design of an up/down counter with asynchronous parallel load and true hold capability, (a) Operation
table, (b) MUX K-map assuming the use of D flip-flops, (c) Logic circuit for the Jth 1-bit slice.
as in Fig. 12.27, the only difference being that the loading is produced asynchronously and
that FET D flip-flops are used.
12.3.6 Perspective on Parallel Loading of Counters and Registers:
Asynchronous vs Synchronous
As has been mentioned or implied at various points in previous discussions, there are two
advantages to asynchronously parallel loading data into the memory flip-flops of registers
and counters. These advantages are as follows:
1. Introducing the parallel data directly into the memory via the preset and clear overrides
of the flip-flops permits the device to change modes of operation before the next
triggering edge of clock. This can save time and speed up the processing of data—
time can be wasted waiting for the data to be clocked input the memory as is required
in synchronously loaded data.