Page 95 - T. Anderson-Fracture Mechanics - Fundamentals and Applns.-CRC (2005)
P. 95
1656_C02.fm Page 75 Thursday, April 14, 2005 6:28 PM
Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics 75
stress, σ = 0 by definition. Under plain strain conditions, σ = 2νσ . Substituting these stresses
zz
zz
yy
into the von Mises yield criterion (Equation (2.82)) leads to the following:
σ (plane stress )
σ (at yield = YS (2.87)
)
yy
2.5 σ YS (plane strain )
assuming ν = 0.3. Therefore, the triaxial stress state associated with plane strain leads to higher stresses
in the plastic zone. For fracture mechanisms that are governed by normal stress, such as cleavage in
metals (Section 5.2), the material will behave in a more brittle fashion when subjected to a triaxial stress
state. Triaxial stresses also assist ductile fracture processes such as microvoid coalescence (Section 5.1).
2.10.2 EFFECT OF THICKNESS ON APPARENT FRACTURE TOUGHNESS
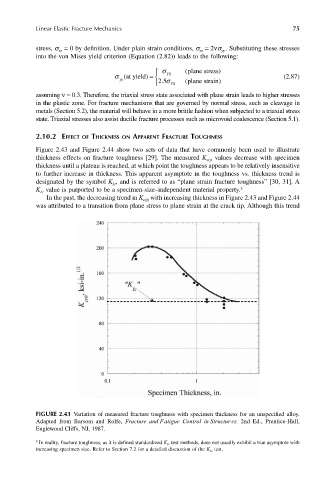
Figure 2.43 and Figure 2.44 show two sets of data that have commonly been used to illustrate
thickness effects on fracture toughness [29]. The measured K values decrease with specimen
crit
thickness until a plateau is reached, at which point the toughness appears to be relatively insensitive
to further increase in thickness. This apparent asymptote in the toughness vs. thickness trend is
designated by the symbol K , and is referred to as “plane strain fracture toughness” [30, 31]. A
Ic
3
K value is purported to be a specimen-size–independent material property.
Ic
In the past, the decreasing trend in K with increasing thickness in Figure 2.43 and Figure 2.44
crit
was attributed to a transition from plane stress to plane strain at the crack tip. Although this trend
FIGURE 2.43 Variation of measured fracture toughness with specimen thickness for an unspecified alloy.
Adapted from Barsom and Rolfe, Fracture and Fatigue Control in Structur es. 2nd Ed., Prentice-Hall,
Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1987.
3 In reality, fracture toughness, as it is defined standardized K Ic test methods, does not usually exhibit a true asymptote with
increasing specimen size. Refer to Section 7.2 for a detailed discussion of the K Ic test.