Page 331 - Fundamentals of Gas Shale Reservoirs
P. 331
RESOURCE EVALUATION OF SHALE GAS PLAYS 311
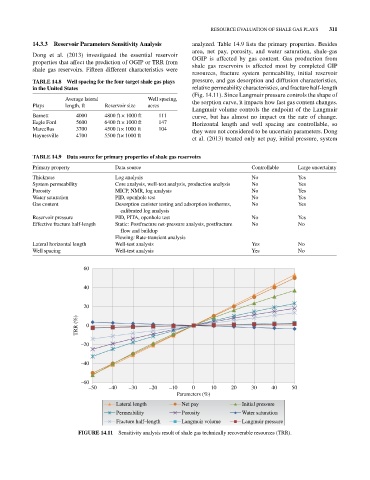
14.3.3 Reservoir Parameters Sensitivity Analysis analyzed. Table 14.9 lists the primary properties. Besides
area, net pay, porosity, and water saturation, shale‐gas
Dong et al. (2013) investigated the essential reservoir OGIP is affected by gas content. Gas production from
properties that affect the prediction of OGIP or TRR from shale gas reservoirs is affected most by completed GIP
shale gas reservoirs. Fifteen different characteristics were
resources, fracture system permeability, initial reservoir
TAbLE 14.8 Well spacing for the four target shale gas plays pressure, and gas desorption and diffusion characteristics,
in the United States relative permeability characteristics, and fracture half‐length
(Fig. 14.11). Since Langmuir pressure controls the shape of
Average lateral Well spacing, the sorption curve, it impacts how fast gas content changes.
Plays length, ft Reservoir size acres
Langmuir volume controls the endpoint of the Langmuir
Barnett 4000 4800 ft × 1000 ft 111 curve, but has almost no impact on the rate of change.
Eagle Ford 5600 6400 ft × 1000 ft 147 Horizontal length and well spacing are controllable, so
Marcellus 3700 4500 ft × 1000 ft 104 they were not considered to be uncertain parameters. Dong
Haynesville 4700 5500 ft × 1000 ft
et al. (2013) treated only net pay, initial pressure, system
TAbLE 14.9 Data source for primary properties of shale gas reservoirs
Primary property Data source Controllable Large uncertainty
Thickness Log analysis No Yes
System permeability Core analysis, well‐test analysis, production analysis No Yes
Porosity MICP, NMR, log analysis No Yes
Water saturation PID, openhole test No Yes
Gas content Desorption canister testing and adsorption isotherms, No Yes
calibrated log analysis
Reservoir pressure PID, PITA, openhole test No Yes
Effective fracture half‐length Static: Postfracture net‐pressure analysis, postfracture No No
flow and buildup
Flowing: Rate‐transient analysis
Lateral horizontal length Well‐test analysis Yes No
Well spacing Well‐test analysis Yes No
60
40
20
TRR (%) 0
–20
–40
–60
–50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0 10 20 30 40 50
Parameters (%)
Lateral length Net pay Initial pressure
Permeability Porosity Water saturation
Fracture half–length Langmuir volume Langmuir pressure
FIGURE 14.11 Sensitivity analysis result of shale gas technically recoverable resources (TRR).