Page 503 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 503
Instrument and control transformers: application and selection 15/477
Any main CT that is underloaded will also add to the measuring CT, a protection CT will have a high saturation
error in the measurement. Similarly, if provision is made level to allow the high primary current to transform
in the primary of the summation CT to accommodate substantially to the secondary as may be required,
future circuits but is not being utilized it must be left depending upon the current setting of the protective or
open. otherwise it will also add to the error. The impedance tripping relays. For protection CTs, therefore, the accuracy
of the shorting terminals will add to the impedance of class is of little relevance up to the primary rated current,
the circuit and will increase the total error. but a true reflection in the secondary is more important
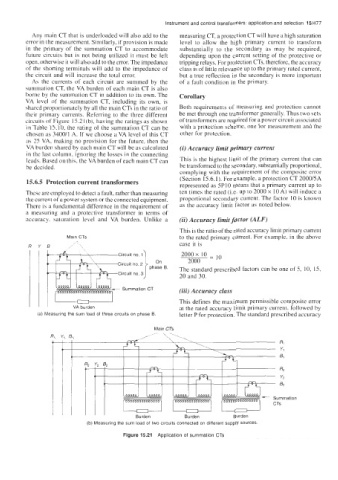
As the currents of each circuit are summed by the of a fault condition in the primary.
summation CT. the VA burden of each main CT is also
borne by the summation CT in addition to its own. The Corollary
VA level of the summation CT, including its own, is
shared proportionately by all the main CTs in the ratio of Both requirements of measuring and protection cannot
their primary currents. Referring to the three different be met through one transformer generally. Thus two sets
circuits of Figure 15.2 1 (b), having the ratings as shown of transformers are required for a power circuit associated
in Table 15.10, the rating of the summation CT can be with a protection scheme, one for measurement and the
chosen as 340011 A. If we choose a VA level of this CT other for protection.
as 25 VA, making no provision for the future, then the
VA burden shared by each main CT will be as calculated (i) Accuracy limit primary current
in the last column, ignoring the losses in the connecting
leads. Based on this, the VA burden of each main CT can This is the highest limit of the primary current that can
be decided. be transformed to the secondary, substantially proportional,
complying with the requirement of the composite error
(Section 15.6.1). For example. a protection CT 2000/SA
15.6.5 Protection current transformers represented as 5P10 means that a primary current up to
These are employed to detect a fault, rather than measuring ten times the rated (Le. up to 2000 x 10 A) will induce a
the current of a power system or the connected equipment. proportional secondary current. The factor 10 is known
There is a fundamental difference in the requirement of as the accuracy limit factor as noted below.
a measuring and a protective transformer in terms of
accuracy. saturation level and VA burden. Unlike a (ii) Accuracy limit factor (ALF)
This is the ratio of the rated accuracy limit primary current
Main CTs to the rated primary current. For example, in the above
P case it is
I\
R Y B ,I' \
,(
2000 x 10 -
-
2000
B. The standard prescribed factors can be one of 5. IO, 15.
20 and 30.
Summation CT (iii) Accuracy class
This defines the maximum permissible composite error
at the rated accuracy limit primary current, followed by
(a) Measuring the sum load of three circuits on phase B. letter P for protection. The standard prescribed accuracy
Main CTs
Rl
Yl
Bi
R2
y2
82
r"""""""l T""""""""i a-
Summation
Burden
Burden
cTs
Burden
(b) Measuring the sum load of two circuits connected on different supply sources.
Figure 15.21 Application of summation CTs