Page 111 - System on Package_ Miniaturization of the Entire System
P. 111
86 Cha pte r T h ree
Materials & Process Challenges
Mechanical Challenges
• Electrical properties
• Dielectric constant • Ultra thin die process
• Loss factor • Assembly-induced stress
• Overhanging configuration in chip stacking
• Insulation resistance
• Electrical conductivity • TCE mismatch between SIP constituents
• Mechanical properties • Distance from neutral point (DNP)
• Thermal coefficient of expansion
• Modulus
• Creep properties
• Thermal properties
• Thermal conductivity
Chip stacking (Non-TSV) Package stacking (Non-TSV) TSV Chip/Wafer stacking
Logic IC
Thermal Challenges Electrical Challenges
• Potential heat transfer paths • Signal integrity
• Less space for power dissipation • Parasitic inductance
• Poor thermal transfer from chip to chip through • Electromagnetic interference (EMI)
polymer adhesives • Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
• High electrical interconnection resistance • Functional partitioning
• Heat sink placement
• Thermal design
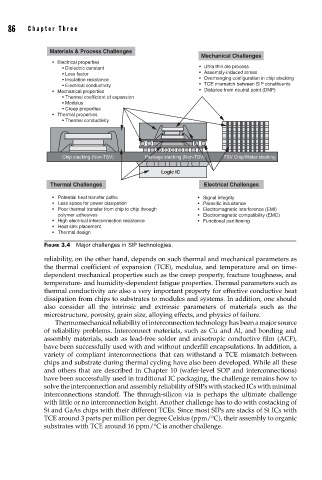
FIGURE 3.4 Major challenges in SIP technologies.
reliability, on the other hand, depends on such thermal and mechanical parameters as
the thermal coefficient of expansion (TCE), modulus, and temperature and on time-
dependent mechanical properties such as the creep property, fracture toughness, and
temperature- and humidity-dependent fatigue properties. Thermal parameters such as
thermal conductivity are also a very important property for effective conductive heat
dissipation from chips to substrates to modules and systems. In addition, one should
also consider all the intrinsic and extrinsic parameters of materials such as the
microstructure, porosity, grain size, alloying effects, and physics of failure.
Thermomechanical reliability of interconnection technology has been a major source
of reliability problems. Interconnect materials, such as Cu and Al, and bonding and
assembly materials, such as lead-free solder and anisotropic conductive film (ACF),
have been successfully used with and without underfill encapsulations. In addition, a
variety of compliant interconnections that can withstand a TCE mismatch between
chips and substrate during thermal cycling have also been developed. While all these
and others that are described in Chapter 10 (wafer-level SOP and interconnections)
have been successfully used in traditional IC packaging, the challenge remains how to
solve the interconnection and assembly reliability of SIPs with stacked ICs with minimal
interconnections standoff. The through-silicon via is perhaps the ultimate challenge
with little or no interconnection height. Another challenge has to do with costacking of
Si and GaAs chips with their different TCEs. Since most SIPs are stacks of Si ICs with
TCE around 3 parts per million per degree Celsius (ppm/°C), their assembly to organic
substrates with TCE around 16 ppm/°C is another challenge.