Page 240 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 240
Sacrificial and Released Structures 219
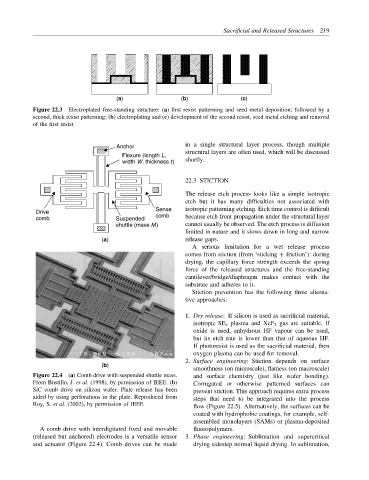
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 22.3 Electroplated free-standing structure: (a) first resist patterning and seed metal deposition; followed by a
second, thick resist patterning; (b) electroplating and (c) development of the second resist, seed metal etching and removal
of the first resist
Anchor in a single structural layer process, though multiple
Flexure (length L, structural layers are often used, which will be discussed
width W, thickness t) shortly.
22.3 STICTION
The release etch process looks like a simple isotropic
etch but it has many difficulties not associated with
Drive Sense isotropic patterning etching. Etch time control is difficult
comb Suspended comb because etch front propagation under the structural layer
shuttle (mass M) cannot usually be observed. The etch process is diffusion
limited in nature and it slows down in long and narrow
(a) release gaps.
A serious limitation for a wet release process
comes from stiction (from ‘sticking + friction’): during
drying, the capillary force strength exceeds the spring
force of the released structures and the free-standing
cantilever/bridge/diaphragm makes contact with the
substrate and adheres to it.
Stiction prevention has the following three alterna-
tive approaches:
1. Dry release: If silicon is used as sacrificial material,
isotropic SF 6 plasma and XeF 2 gas are suitable. If
oxide is used, anhydrous HF vapour can be used,
but its etch rate is lower than that of aqueous HF.
If photoresist is used as the sacrificial material, then
oxygen plasma can be used for removal.
2. Surface engineering: Stiction depends on surface
(b)
smoothness (on microscale), flatness (on macroscale)
Figure 22.4 (a) Comb drive with suspended shuttle mass. and surface chemistry (just like wafer bonding).
From Bustillo, J. et al. (1998), by permission of IEEE. (b) Corrugated or otherwise patterned surfaces can
SiC comb drive on silicon wafer. Plate release has been prevent stiction. This approach requires extra process
aided by using perforations in the plate. Reproduced from steps that need to be integrated into the process
Roy, S. et al. (2002), by permission of IEEE flow (Figure 22.5). Alternatively, the surfaces can be
coated with hydrophobic coatings, for example, self-
assembled monolayers (SAMs) or plasma-deposited
A comb drive with interdigitated fixed and movable fluoropolymers.
(released but anchored) electrodes is a versatile sensor 3. Phase engineering: Sublimation and supercritical
and actuator (Figure 22.4). Comb drives can be made drying sidestep normal liquid drying. In sublimation,