Page 156 -
P. 156
146 4 Optical Rotor
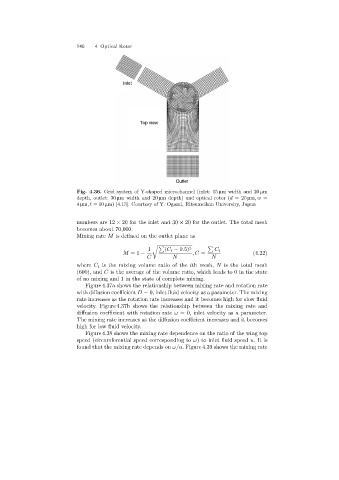
Inlet
Top view
Outlet
Fig. 4.36. Grid system of Y-shaped microchannel (inlet: 15 µm width and 20 µm
depth, outlet: 30 µm width and 20 µm depth)and optical rotor (d =20 µm,w =
4 µm,t =10 µm)[4.13]. Courtesy of Y. Ogami, Ritsumeikan Universiry, Japan
numbers are 12 × 20 for the inlet and 30 × 20 for the outlet. The total mesh
becomes about 70,000.
Mixingrate M is defined on the outlet plane as
1 % (C i − 0.5) 2 % C i
M =1 − ,C = (4.22)
C N N
where C i is the mixingvolume ratio of the ith mesh, N is the total mesh
(600), and C is the average of the volume ratio, which leads to 0 in the state
of no mixingand 1 in the state of complete mixing.
Figure 4.37a shows the relationship between mixing rate and rotation rate
with diffusion coefficient D = 0, inlet fluid velocity as a parameter. The mixing
rate increases as the rotation rate increases and it becomes high for slow fluid
velocity. Figure 4.37b shows the relationship between the mixing rate and
diffusion coefficient with rotation rate ω = 0, inlet velocity as a parameter.
The mixingrate increases as the diffusion coefficient increases and it becomes
high for low fluid velocity.
Figure 4.38 shows the mixingrate dependence on the ratio of the wingtop
speed (circumferential speed correspondingto ω) to inlet fluid speed u.Itis
found that the mixingrate depends on ω/u. Figure 4.39 shows the mixing rate