Page 251 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 251
Circuit Design 223
SigA can cause a second transition of SigB, which must occur after flip-
flop capturing SigB is closed. The amount SigB is later than needed is
the mindelay timing margin.
A mindelay violation is also called a race because a single clock tran-
sition causes two things to happen. One clock edge makes the input to
the flip-flop switch and causes the flip-flop to capture data. One event
must happen before the other for the circuit to function properly, and it
is the race between these two events that must be checked. This makes
mindelay violations particularly worrisome because changing the clock
frequency will have no effect on them. Slowing down the clock and allow-
ing more time for signals to propagate through the logic of the pipestage
can fix a maxdelay violation. This will mean selling the processor at a
lower frequency for less money, but the processor is still functional. A
mindelay violation is independent of the clock frequency and usually
forces a processor to be discarded.
Because there are many possible paths through a circuit, a single
pipestage can have maxdelay and mindelay violations at the same time.
Much of a circuit designer’s effort is spent balancing the timing of cir-
cuits to meet the project’s frequency target, without creating mindelay
violations.
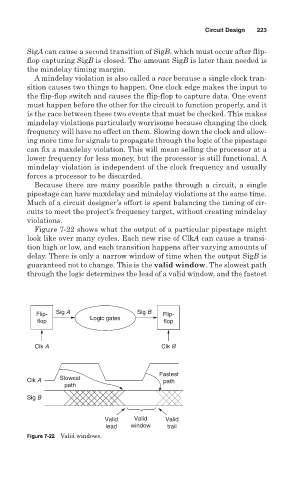
Figure 7-22 shows what the output of a particular pipestage might
look like over many cycles. Each new rise of ClkA can cause a transi-
tion high or low, and each transition happens after varying amounts of
delay. There is only a narrow window of time when the output SigB is
guaranteed not to change. This is the valid window. The slowest path
through the logic determines the lead of a valid window, and the fastest
Flip- Sig A Sig B Flip-
flop Logic gates flop
Clk A Clk B
Fastest
Slowest
Clk A path
path
Sig B
Valid Valid Valid
lead window trail
Figure 7-22 Valid windows.